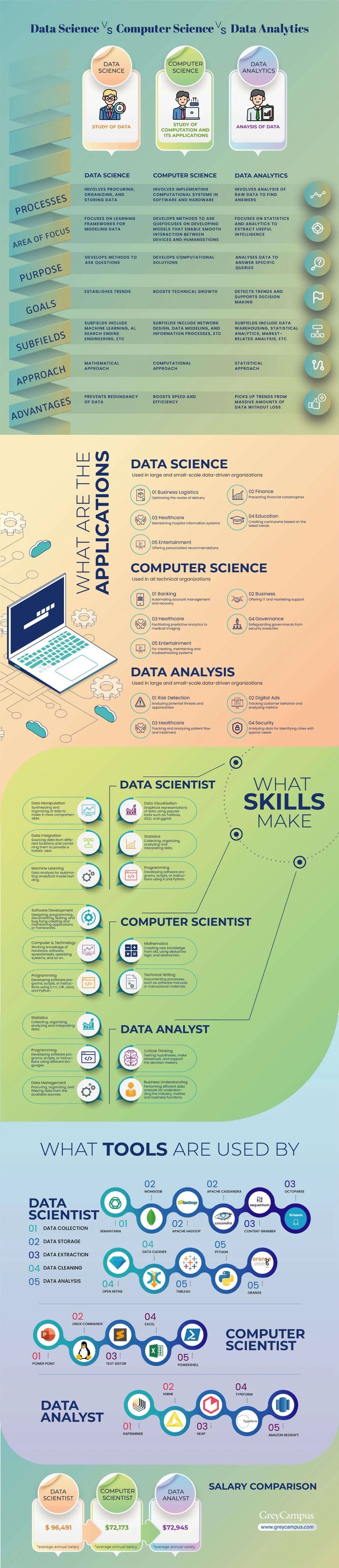
Data Science vs Computer Science vs Data Analytics: A Breakdown
Summary
Table of Content
With the pandemic steering the world towards technology-based solutions, the tech sector has experienced significant growth. Of the endless career possibilities in the sector, data science, computer science, and data analytics are three prominent fields currently taking center stage. These domains are now responsible for influencing critical decisions and driving success in both small-scale and large-scale organizations.
Now, how do these fields differ from each other? Are they subsets of a single discipline?
Here is a breakdown of the three fields: data science vs. data analytics vs. computer science, the skills you need, what these fields entail, and how you can springboard your career in each.
What is Data Science?
As data is the new fuel that powers businesses across all industries, data science has emerged as something businesses can’t do without. Data science is the ultimate solution to unearth useful intelligence from the data available online; these insights are then used to add value to the business or the organization. Data science relies on algorithms and scientific methods to extract useful business insights from available data.
What Are the Applications of Data Science?
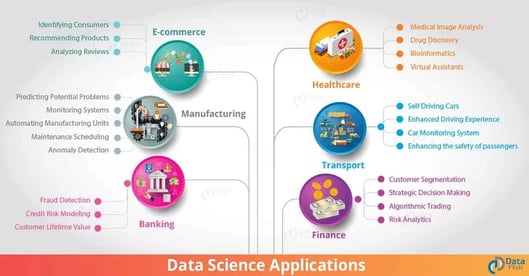
The cutting-edge technology of data science has transformed and redefined the nature of solutions in a wide range of industries. Here are 5 major applications of data science:
1. Data Science in Business Logistics
Business logistics is one sector in which data science can have a significant influence on waste reduction. Optimizing the routes of delivery, choosing carriers that mitigate the effects of CO2 emissions, safeguarding hazardous materials, and predicting the supply and demand are some ways business logistics use data science.
2. Data Science in Finance
Data scientists have been saving financial entities from catastrophes for a while now. Be it the detection of fraudulent activities or monitoring risks, data science can shield financial institutions from potential threats. These organizations also rely on data scientists during economic recessions, where their analytic skills are used to arrive at make-or-break decisions.
Source: DataFlair
3. Data Science in Health
From medical imaging to predictive analytics in healthcare, data science has a lot of applications in the health sector. Pharmaceutical industries use machine learning and its algorithms to create models and find statistical relationships. The algorithms can then simulate the impacts of a drug on a patient’s body.
4. Data Science in Education
Data science is used to understand the trends and patterns in industries and tweak the curriculum to accommodate them. Data science also powers student assessment by helping instructors capture the patterns of student performance. Based on the inference, teachers can alter their teaching methods.
5. Data Science in Entertainment
It is no surprise that the entertainment industry is now data-driven; massive amounts of customer data are now available online, paving the way for the progress of data science in the sector. OTT (over-the-top) platforms like Netflix and Hulu depend on data to personalize the applications for users. The top picks you see on your device is the work of data science.
The same data is also used for customer segmentation or the classification of customers based on the content they consume. Data science is also used to predict the viewership of content based on which shows can be scheduled.
Data Science Lifecycle: Definition and Steps
The data science lifecycle refers to a series of processes that are followed by data scientists to deliver a data science project.
The following steps are involved:
Step 1 ─ Data Collection
This step is the foundation of your data science project. Incomplete data is unreliable data; failing to procure valid data from relevant data sources is a critical task. Since data storage is not expensive these days, the idea is to collect everything you can get your hands on and filter out relevant data.
Step 2 ─ Data Preparation
The data that you acquire in the first step is not usable; it has to be organized. In this stage, the quality issues of data are identified and solved. There could even be semantic errors, missing entries, or inconsistencies. The data sets are integrated and structured for analysis.

Source: Sudeep.co
Step 3 ─ Exploratory Data Analysis
Data is analyzed at this stage to extract useful information. Based on your analysis of the information, decisions are made. There are no hard and fast rules in this process; but the more effort and time you dedicate to this process, the better your decisions will be.
Step 4 ─ Model Building
This is the core process in the data science lifecycle. After identifying the nature of the problem, an appropriate data model and algorithm are chosen. The parameters are then tweaked to achieve the desired outcome.
Step 5 ─ Model Deployment
This is the stage where a data science project gets deployed in the real world through an iOS or Android app. Machine learning projects are first deployed in a test environment and later pushed into production.
You may also like: Data Science Master Guide: Top 10 Tips to Ace Your Interview Like a Pro.
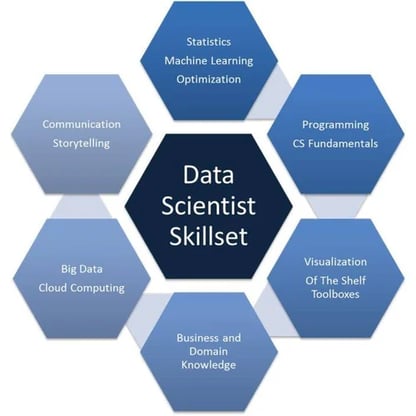
What Skills Does a Data Scientist Need?
The title ‘data scientist' was first used in 2008 to refer to professionals who were skilled at analyzing and organizing data. Today, data scientists are some of the most sought-after professionals in the tech sector. They are data-driven professionals who possess extraordinary domain expertise and technical skills.
A data scientist is adept at filtering out relevant information, identifying important questions, procuring data from a variety of sources, and eventually translating it into positive results. With the growing application of data science in all industries, these professionals now enjoy great demand in the industry.
You need the following skills to handle data science projects:
1. Data Manipulation and Data Integration
Data manipulation is the synthesizing and organizing of data to make it more comprehensible. To map data the right way, a data scientist needs to master a programming language called data manipulation language (DML). This language is used to manipulate data by adding, deleting, and modifying it.
Data integration is the process of sourcing data from different locations and combining it to provide a holistic view. This skill is vital to gather business intelligence. Being exceptional at data integration can help you land a job in highly reputable organizations.
2. Machine Learning (ML)
Organizations that are grounded in data-centric decisions are always on the lookout for data scientists who are good at machine learning. Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence and contributes heavily to data modeling by employing algorithms. A thorough understanding of machine learning techniques, such as logistic regression and decision trees, will help you stand out in the industry.
3. Data Visualization
The online business world is flooded with data that has implicit information. This data needs to be gathered first and then presented in a comprehensible visual format. Data visualization is one of the primary tasks a data scientist performs in which he or she creates interactive visualizations to learn trends, patterns, and variations. The inferences made from these visualizations are then shared with stakeholders to make decisions. Tableau, d3.js, and ggplot are some common data visualization tools.
Source: Cleanpng
4. Statistics
Statistics is an inevitable part of a data scientist’s toolkit. Being well-versed in statistics enables you to effortlessly procure, organize, analyze, and filter out information from the data. You need a thorough understanding of the fundamental concepts and principles of statistics, such as percentiles and outliers, cumulative distribution function (CDF), exploratory data analysis, Bayes theorem, probability theory, random variables, and descriptive statistics.
5. Programming
Programming is a must-have skill for data scientists. Though Python is regarded as the gold standard in programming languages, data scientists also need to be proficient in R programming languages. Python is an object-oriented language that is very easy to deploy, while R is an open-source language that is used for statistical analysis.
6. Business Understanding
An in-depth understanding of the business, as well as the industry, is a mandatory requirement in data science. To be able to identify the right questions, analyze problems, and seize business opportunities, a data scientist must have refined business acumen.
Salary Trends in Data Science
Data science is one of the highest-paying jobs in the world. 68 percent of data scientists reported that their pay scale was enough to cover their living expenses. In the United States, the average annual salary of a data scientist is $96,491.
There could be slight variations in remuneration depending on your organization’s location and your experience. Remember that data scientists with advanced educational qualifications earn more. With a Master’s or a Ph.D., you can easily land a senior role in a reputable organization.
What Tools Are Used in Data Science?
Data scientists need tools to apply their operational knowledge and methods to data. Here are some of the popular data science tools used by data scientists.
1. Data Collection Tools
While interviews and surveys remain conventional methods of data collection, the following are two favorite data collection tools of data scientists:
- Trackur ─ It collects data on social media platforms from feedback on products or services. It serves as a monitoring tool for marketing companies.
- Semantria ─ It analyzes texts and sentiments to extract useful data and information. It is cloud-based which uses top-notch neuro-linguistic programming (NLP).
2. Data Storage Tools
Data storage tools are used to store data in large amounts. These tools allow data scientists to unite servers and assess for easy access to data. The following are data storage tools:
- MongoDB ─ It is a free-to-use, document-oriented tool that is available on Linux, Solaris, and Windows.
- Apache Hadoop ─ It is a software framework that can handle large amounts of data and its computation. It allows easy distribution of data for processing.
- Apache Cassandra ─ It is an open-source, free tool that uses CSL and SQL to communicate with databases. It allows easy access to data that is stored on various servers.

Source: DataFlair
3. Data Extraction Tools
Data extraction tools or web scraping tools are automated tools that are used to extract useful data from websites. The following are two popular data extraction tools:
- Content Grabber ─ It is a data extraction tool that comes with added features like error handling and debugging. It can extract data and provide it in structured forms in your preferred format.
- OctoParse ─ Available in both paid and free versions, OctoParse is a web scraping tool that extracts and delivers data in spreadsheets. The data is presented in easy-to-read formats.
4. Data Cleaning Tools
Data cleaning tools are used to search, filter, and organize data. The following are data cleaning tools:
- OpenRefine ─ This tool refines tangled data and sorts it out before transforming it into a usable format.
- DataCleaner ─ This is a data indexing tool that works alongside the Hadoop database. It prevents duplication of data and finds missing patterns.
5. Data Analysis Tools
These tools are inevitable for decision-making; they analyze and inspect data to derive insights. The following are common data analysis tools:
- Tableau ─ This is an open-source tool that is used for the visualization of data in maps, charts, bars, etc.
- Python ─ Python is a general-purpose language that is also used for data visualization. It contains graphical libraries to enable visualization.
- Orange ─ It is an open-source tool that is used for analyzing data. It is user-friendly and has a graphical interface to support data visualization for analysis.
You may also like: Top 10 Libraries of Python for Data Science
What is Computer Science?
Computer science is the scientific study of computers, software, hardware, and their algorithmic and theoretical foundations. It also involves disciplines such as artificial intelligence, network design, data modeling, and information processes. Grounded in mathematics and engineering, computer science has multiple subfields that overlap.
What Are the Applications of Computer Science?
It goes without saying that the world would come to a standstill in the absence of computers. There is hardly any industry that does not utilize the fruits of this invention. Initially used to handle complex calculations, computers are now ubiquitously applied across all industries to simplify our lives.
Let’s dive into some applications of computer science.
1. Computer Science in Banking
Automated account management revolutionized the banking sector. Thanks to computer science, bank personnel can now create and maintain accounts easily. Customer transactions now involve a centralized record, helping banks to track things easily. Computer science has also made it possible for smaller financial entities to access the same technology as larger financial institutions, enabling fair business competition.
2. Computer Science in Business
Be it the IT support in business organizations or the marketing tactics employed by the marketing team, computer science is inevitable in the world of business. With online businesses taking the world by storm, having an online store pays off more than an actual store. Not only do businesses appear more streamlined when you have the know-how to maintain an online store, it saves time and cuts costs.
3. Computer Science in Medicine
The most remarkable social impact of computer science is in the field of medicine and healthcare. Taking care of patients in critical situations, medical imaging, decision-making, and maintaining hospital information systems are some prominent applications of computer science in medicine.
You may also like: Beautifulsoup: A step-by-step guide to Data Scraping with Python
4. Computer Science in Government
Computer science has an array of applications in government. With the world depending on computer science now more than ever, governments need computer scientists to run smoothly. They maintain government websites, safeguard them from security breaches, keep records of the country and its population, and support decision-making.
5. Computer Science in Entertainment
Computer science creates, maintains, and troubleshoots all systems that make entertainment; it is the foundation of the modern entertainment industry. The demand for computer science professionals are reportedly increasing in industries like Hollywood. Professional editing software programs paved the way for efficient non-linear editing of movies. Special effects are now an important part of the industry; VFX artists add the desired graphics that can blend in easily with the scenes.
What Skills Do You Need to be a Computer Science Professional?
You need the following skills to be a computer science professional:
1. Software Development Skills
Having software development skills on your resume is one of the easiest ways to catch the attention of your potential employers. It tells them that you can write codes and programs, test, and deliver functional software programs.
2. Math Skills
Computer science is founded upon mathematics. You need a fair understanding of math to grasp computing formulas. Being good at math comes in handy when you encounter complex problems.
3. Technical Writing Skills
Skills to create computer-based solutions are not enough; you also need to be an effective communicator to explain the challenges to other team members. With good technical writing skills, you can meticulously write reports, give presentations, and even train others.
4. Computer and Technology skills
Basic computer and technology skills are necessary to do well in any IT role. This includes hardware, software, spreadsheets, and operating systems. An IT professional cannot be relied on if he or she lacks the foundational knowledge of these aspects.
5. Programming Skills
You need programming and coding languages to frame instructions and design your software program. C++, C#, Java, and Python are common programming and coding languages you can add to your resume. This shows your technical expertise to your potential employers.
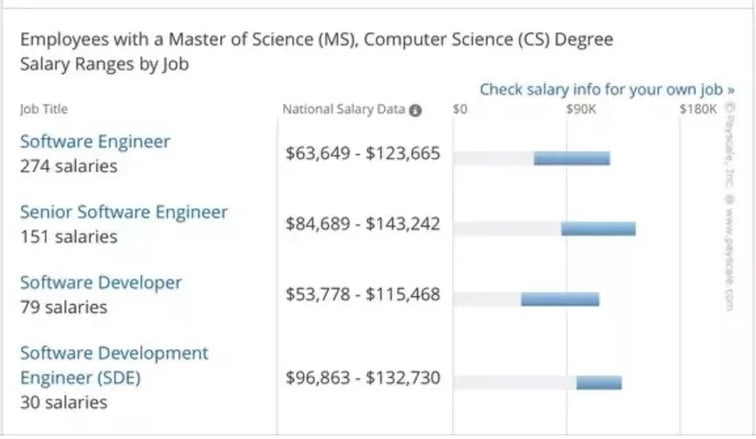
Salary Trends in Computer Science
What is the salary trend in the computer science market? According to NACE’s survey of 2021, computer science majors are of great value in today’s virtual world; the pandemic has only increased this. While most roles only need a Bachelor’s, you need a Master’s to land managerial positions.
Source: PayScale
$72,173 is the average annual salary of computer science graduates. All three computer science majors (computer science, information sciences and systems, and software applications) saw a considerable increase in the average salary projection (6.8 to 7.1 percent) in recent years.
What Tools Are Used in Computer Science?
The following are tools used in computer science.
1. PowerPoint
PowerPoint is an essential tool for all IT professionals, including software developers, business analysts, quality assurance analysts, and project managers. This tool is effectively used for presentations, training sessions, discussions, or even sharing plans with managers.
2. Linux Commands
Foundational knowledge in Linux commands makes you self-reliant; not only can you analyze the problems you face, but you can also troubleshoot them with Linux commands.
3. Text Editor
IT professionals like software developers handle a lot of text processing. Mastering basic text editors like NotePad is imperative. But it is always recommended to learn advanced text editors such as NotePad++ or Sublime.
4. Excel
Excel is one of the most popular Office tools and is not merely a spreadsheet application. From quality assurance to project management, a lot of IT roles use Excel to create reports and automate tasks.
5. PowerShell
Developed by Microsoft, Windows PowerShell automates tasks and configures management processes. This tool is built on the .NET framework and comes with a command-line shell and scripting language.
How to Begin Your Career in Computer Science?
1. Choose the right degree. Computer science has multiple subfields that interrelate. Though these fields might overlap, the skills required to excel in each of these domains vary. Is computer science hard? Not really; depending on your aptitude and skills, you can narrow your career path in computer science. With a Master’s or other advanced degrees, you don’t have to settle for entry-level computer science jobs.
2. Develop in-demand skills. After you graduate, investigate the demands of your industry to keep up with the trends. To stay employable, you need to investigate the skills that your potential employers are seeking in a candidate. This could include specialization in a certain area or even professional certifications.
3. Know what you need; contemplate your interests. Try to arrive at a conclusion regarding what sort of IT ecosystems you are aiming to work in. Ask yourself if you are interested in the coding and developing aspects or the commercial end of businesses. Come to a decision regarding want you want to create; do you want to create a product from scratch or develop somebody else’s idea?
4. Highlight your resourcefulness in your resume; make sure your resume sheds enough light on your resourcefulness, in-demand technical skills, experience, and soft skills. Be very specific about your educational qualifications.
5. Build and maintain a network; building networks with professionals will help you increase your access to opportunities. Staying in their good graces and presenting yourself as an employable candidate will help you land a job.
6. Ace Your Interview. Prepare a digital portfolio that demonstrates your skills and expertise. Be ready for a coding challenge. Never lie; make sure you are transparent about your skills and shortcomings.
Data Analytics
Data analytics refers to a set of techniques that are employed to make conclusions from raw data through analysis. It involves automated algorithms and mechanical processes that can detect metrics that could be easily lost in massive amounts of data. Cartesian Consulting, Absolutdata, Convergytics, and Crayon Data are the biggest data analytics companies.
Applications of Data Analytics
1. Data Analytics in Risk Detection
Data analytics is one of the finest methods to detect fraudulent activities and risks. It is used to learn expenditure, examine customer profiles, and analyze potential threats and probabilities of a customer engaged in defaulting activities.
2. Data Analytics in Medicine
Healthcare has always been a costly affair. Hospitals spend a lot of money when it comes to machines and medicines. But with data analytics, they can now track patient flow and treatment.
3. Data Analytics in Digital Ads
The digital ads that you see on your devices are the result of the intervention of digital analytic techniques. Ad creators use analytics to track customer behavior and plug-in ads wherever necessary for impressive click-through rates (CTRs).
4. Data Analytics in Security
Data analytics is used to reinforce security in cities with the highest crime rates. The police tap into geographical and historical data to single out cities that need special attention; these areas are then given special patrols.
What Skills Does a Data Analyst Need?
1. Statistics
Data analytics is heavily dependent on the statistical analysis of data. Though different IT roles demand different kinds of math skills, a data analyst needs exceptional quantitative skills to solve practical problems.

Source: Bootcamp CVN
2. Programming
Since automated software applications may not be powerful enough to solve complex problems, data analysts need to learn the techniques of programming. They might need to create codes on their own that could address the problems of a specific data set.
3. Data Management
Data analysts must be skilled at procuring, organizing, and filtering data. They also need to be experts at extracting the data sets they need from large chunks of data available online.
4. Critical Thinking
Data analysts are critical thinkers who can test hypotheses, make inferences, and support decision-makers. They need to be skilled at translating the demands of the business into questions about data.
5. Business Understanding
In order to perform efficient data analysis, data analysts need to have a thorough understanding of the industry, market, and business functions. This will enable them to face challenges and make appropriate decisions.
Salary Trends in Data Analytics
As data analysts are in high demand, organizations are willing to adapt their pay scales because of the critical tasks these professionals perform. The average base salary of a data analyst is $72,945. Organizations like Facebook, Target, and Intuit pay data analysts more than $100,000. Your certifications, educational qualifications, and experience have considerable influence on your pay scale.
What Tools Are Used in Data Analytics?
The following are important data analytics tools in a data analyst’s toolkit:
1. RapidMiner
ReapMiner is an open-source platform used for machine learning and data mining. It is based on visual programming and allows the creation of analytical workflows.
2. KNIME
With countless modules and usable demos, KNIME is an open-source analytics tool. It has a large collection of algorithms and is most useful in data mining experiments.

Source: DataFlair
3. Heap
Heap is used to tap into customer behaviors and patterns and track taps, clicks, swipes, mouseovers, and other actions to capture data.
4. Typeform
Typeform is a popular survey form tool. You can create custom forms to conduct surveys. This tool then integrates with MailChimp and Google Sheets to provide you with insights.
5. Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift is primarily used for Big Data and serves as a data warehouse for relational databases. It is a framework that distributes data on different servers in a single cluster.
You may also like: 9 Must-Have Data Analysis Tools To Create Dashing Business Reports
How to Begin Your Career in Data Analytics?
1. Earn your degree with an emphasis on analytical and statistical skills. The greater your qualifications, the better your job will be.
2. Study your industry; understand how success is usually defined in your niche. Work towards getting into your dream companies. Follow their blogs and accomplishments.
3. Develop in-demand technical and soft skills. Follow industry trends to keep track of the most attractive skills. Learn to code; being proficient in reading, writing, and analyzing code is an important skill.
4. Get professional certifications; most organizations demand specialized professional skills. You can make it to reputable organizations with globally recognized certifications in data analytics. These certifications will not only help you land jobs but stay relevant in your industry.
5. Maintain a network with professionals from your industry. You can even reach out to people on online forums for referrals, suggestions, or interviews.
Data Science vs. Data Analytics vs. Computer Science: Some Interesting Statistics
Due to the increased use of technology-driven services, data science, data analytics, and computer science have grown significantly in recent years. Here are some interesting statistics to prove this.
- According to a recent survey by Dice, the demand for data scientists increased by 50 percent last year across multiple industries. Data science significantly simplified the transition from on-site work to virtual/remote working.
- Data science is one of the top 20 fastest-growing disciplines, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
- A report by Deloitte Access Economics found that 76 percent of business organizations plan to spend a considerable amount of time on data analytics over the next two years.
- According to a Forbes article, organizations that use data analytics to make decisions are expected to have a higher growth rate.
- Computer science careers are expected to grow by 13 percent in the next five years.
- There will be an additional 557,100 new jobs in computer science and allied fields.
Data Science vs. Computer Science vs. Data Analytics: A Comparative Analysis
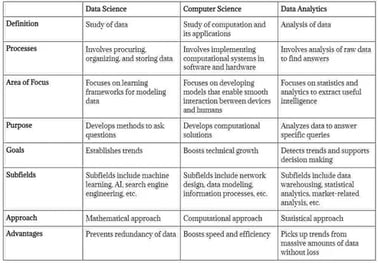
Whether earning potential or job satisfaction, data science, data analytics, and computer science makes good career options. If you lean more toward data science, you can have rewarding career growth with professional certifications. GreyCampus is a leading provider of online career training programs in data science. Its Data Science Foundation program and Data Science career program are project-based intensive courses led by industry veterans. The courses ensure hands-on project experience and are also ideal for professionals seeking remote data science jobs.
Want a Data Science job? Sign Up for OdinSchool's Data Science Bootcamp now!