Top 20 Trending Computer Forensics Tools of 2018
Introduction
The word “Forensics” refers to the techniques used by the investigators to solve a crime. Every invention has its pros and cons. Computers and electronic devices have evolved much faster, and are being used in modern crimes. The art of investigating a crime, conducted with or involving computers, is called computer forensics. To be precise, it is the technique used to extract and preserve evidence from the devices and subsequently present it in the court of law. Computers are both a target and a weapon. Attackers have evolved, they are using sophisticated computer systems to commit such heinous phishing crimes (Here's a resource that will navigate you through cyber security attacks). The target can be a home system, corporate network or even all the computers that they can connect to it. With this increasing rate of crime involving computers, evidence collection has become a vital part. This calls for expert computer forensic professionals.
What are computer forensics tools?
These are the tools that have been developed by programmers to aid digital evidence collection. These tools have evolved and can perform all kinds of activities– from basic to advance level. Forensic tools can be categorized on the basis of the task they perform.
- Network Forensic tools
- Database analysis tools
- File analysis tools
- Registry analysis tools
- Email analysis tools
- OS analysis tools
- Disk and data capture
We will be discussing about 20 forensic tools in some detail later in this article.
What is the work of a forensic investigator?
The major task of a forensic investigator is to find and preserve the data evidence. He should be well versed with the procedures and protocols to be followed:
At the crime scene,
- Evidence collection and handling
They gather and preserve physical evidence, and document their activities.
In the laboratory,
- Evidence analysis
They examine what they have gathered.
They try to reconstruct what happened.
In court of law
- Evidence presentation and reporting
Follow strict standards so their work is acceptable to the court. They can be called to testify about their findings and methods.
Classification of Forensic tools
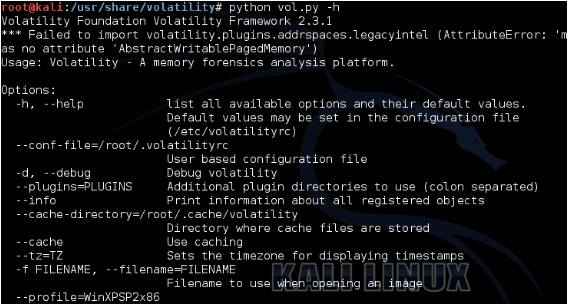
1. Volatility
Volatility is an open source framework used to perform volatile memory forensics. It is written in Python and supports almost all 32 and 64bit machines. Full list of systems supported by volatility can be found at http://www.volatilityfoundation.org/faq
It can perform reconnaissance on process lists, ports, network connections, registry files, DLL’s, crash dumps and cached sectors. It can also analyze system hibernation files and can check for root kit presence as well. You can download the volatility framework from https://code.google.com/archive/p/volatility/downloads
It is already present in Linux kali under the forensic section. Below is a snapshot of volatility.
2. EnCase
Encase is a multipurpose forensic investigation tool. It can help forensic investigators across the investigation life cycle:
- Forensic triage: Prioritizing the files for investigation basis volatility and few other parameters.
- Collect: Collection of digital data without compromising the integrity.
- Decrypt: Ability to analyze encrypted data files by decrypting them. This is done by using password recovery mechanisms.
- Process: Helps in indexing the evidence and in automating common tasks so that time can be spent on investigation rather than the process.
- Investigate: It can perform investigation for almost all windows and mobile operating systems.
- Report: Create a report that will serve all audience. The report must have reporting templates with various format options.
The tool is not free and the price can be requested here: https://www.guidancesoftware.com/encase-forensic
3. MailXaminer
As the name suggests, MailXaminer is used to perform email analysis. It can examine emails from both web and application based mail clients. It helps the investigator in- collecting email evidence, arranging the evidence, searching the emails using various advanced options like Regex. It has the ability to detect and report obscene image attachments by using skintone analysis. It can support 20+ email formats and can generate the report with evidence in the required format. This can assist in closing the case in a court of law.
This is not a free tool but the evaluation version can be downloaded from: https://www.mailxaminer.com/
Image source: https://lscnetwork.blog
4. FTK
FTK or Forensic toolkit is used to scan the hard drive and look for evidence. FTK is developed by AccessData and has a standalone module called FTK Imager. It can be used to image the hard disk, ensuring the integrity of the data using hashing. It can image the hard disk in a single file for files in multiple sections, that can be later joined to get a reconstructed image. Investigators can chose between GUI or command line as per convenience.
More information about FTK can be accessed at https://accessdata.com/products-services/forensic-toolkit-ftk
5. REGA
REGA is used for performing windows registry analysis. The freeware version can be downloaded from http://forensic.korea.ac.kr/tools/20151030_REGA_Freeware.zip
It is a GUI based application. User can create a case and load the registry. The registry can be searched using filters, or manually using timestamps. REGA features:
- Data collection: Collect target registry files for enumeration and analysis.
- Recovery: Recover registry for deleted keys.
- Analysis:
- Windows analysis: Owner, Installation data, etc.
- Storage analysis: Accounts present, run commands, browser history analysis (URLs).
- Network connection analysis: network drive connections, etc.
- Application analysis: List of auto runs, application usage history, etc.
- SW and HW management: Software and hardware installations, storage devices connections.
- Reporting: Create result reports in CSV formats.
The tool is written in C/C++ and is available in English, Korean and Japanese languages.
6. Bulk Extractor
Bulk extractor can be used for extracting important information from files and hard drives. The tool can perform a scan irrespective of the hierarchy of files. Bulk Extractor comes installed in Kali Linux, it can also be installed manually on other OS.
Link to Git: https://github.com/simsong/bulk_extractor
Bulk extractor creates an output directory that includes information about credit card, Internet domains, emails, MAC addresses, IP addresses, Images and videos, URL’s, telephone numbers, searches performed, etc.
7. Oxygen Forensics
Oxygen Forensic Suite is used to gather digital evidence from mobile phones and cloud services used on phones. The suite can bypass Android screen lock, get location history, extract data from cloud storages, analyze call and data records, search data keywords, recover deleted data and export data to various file formats. It supports various mobile platforms including Android, Sony, Blackberry and iPhone.
It generates easy to understand reports for easier correlation.
Visit official website for more info: https://www.oxygen-forensic.com/en/
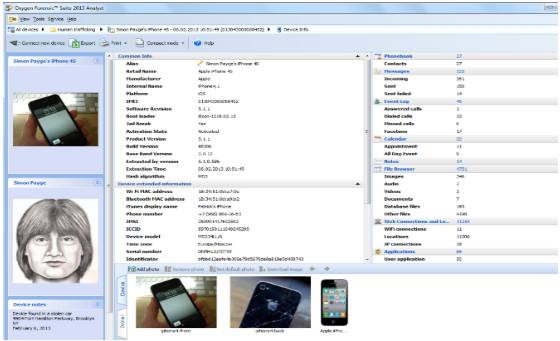
Image source: http://www.dataforensics.org
8. FireEye RedLine
RedLine was originally the product of Mandiant organization, later taken over by FireEye. This is a freeware tool which can be used to perform memory and host analysis for traces of infection, or any malicious activity.
It can be used to collect and correlate information about the running processes, memory drives, registry, file system metadata, event logs, web history and network activity. It can shortlist the processes using malware risk index score, and then investigate them further.
Read more here: https://www.fireeye.com/services/freeware/redline.html
9. Autopsy
Autopsy is an open source digital forensic software, it is used for conducting hard drive investigations. It is used by various law enforcement agencies, military and government and corporate investigators to conduct digital investigations. The company also provides custom development and training to help the users take full advantage of the tool. It is present for both Windows and Linux, and is pre-installed in Kali Linux as well.
The windows version can be downloaded from: https://www.autopsy.com/download/
The tool is built for ease of use and to provide extensibility- user can customize the tool, and is able to add new functionality by creating plug-ins. Autopsy has 3 versions as of now and version 2 relies on the Sleuth Kit to perform disk analysis.
Further information about the Sleuth kit is available at: https://www.sleuthkit.org/autopsy/
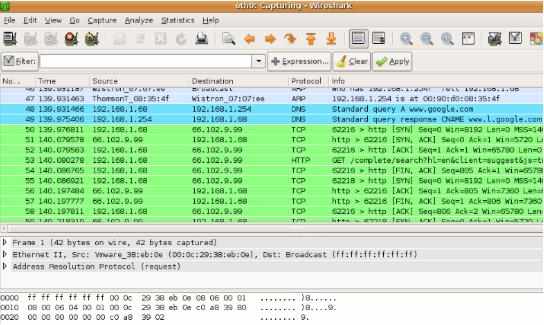
10. Wireshark
Wireshark is used to capture and analyze network traffic. This is done using libPcap and winPcap which captures the network packets. The network packets can then be analyzed for malicious activity. The tool offers the ability to filter the traffic using various filters, it is done based on protocols, string presence, etc.
The tool can be downloaded at: https://www.wireshark.org/download.html
11. USB Write Blocker
As the name suggests, USB write blocker is used for the forensic investigation of storage drives. The maximum it can analyze is 2TB. It is a hardware device as opposed to the rest of the tools that are being discussed. It is used to clone and analyze storage, ensuring data authenticity.
12. X-Ways Forensics
X-ways is a German product and has a lot of features, it can be considered an exhaustive tool. The tool does not use many resources compared to the features it offers. It can be used for- disk imaging and analysis, analysis of various disk formats, case management, registry view, metadata extraction, etc.
For complete feature set refer: http://www.x-ways.net/forensics/
13. DumpZilla
Dumpzilla is used to collect and analyze browser information, including browser history. The tool is developed in Python 3.x and is available for both windows and linux. The investigation scope is not limited to browser history, it also includes cookies, proxy settings, web forms, bookmarks, cache, add-ons, saved passwords, etc.
14. ExifTool
ExifTool is used to gather and analyze metadata information from various images, audio and PDF files. It is both available in command line and GUI versions. Simply execute the application for windows and drag & drop the files which are to be analyzed. The list of file formats that can be analyzed with this tool is exhaustive. The full list is available at: https://www.sno.phy.queensu.ca/~phil/exiftool/
The tool is fast and small in size compared to the functionality provided.
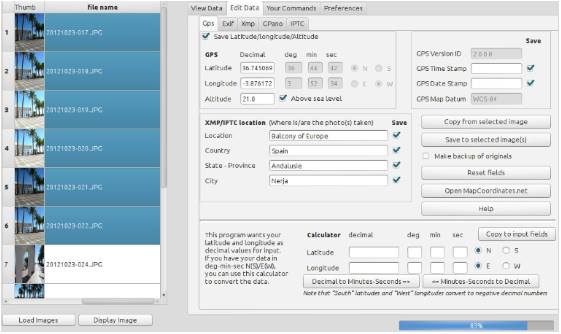
Image source: https://hvdwolf.github.io
15. Binwalk
Binwalk is used for searching a binary image of embedded files in .exe code. The tool is capable of extracting all the files present in the firmware to perform a string search. The tool is powerful enough when coupled with various other tools, and is a must in a forensic investigator toolkit.
16. Hashdeep
Hashdeep is used to generate, match and perform hash auditing. Other programs will report if a hash is matched or missed, but Hashdeep can provide a detailed view of the big picture. It can help us identify matched files, missed files, find hash collisions and various other attributes of the hashes. Keep this with you as integrity of the files is of utmost importance in these cases.
17. Volafox
Volafox is used for MAC OS X memory analysis. It can help in- finding kernel extensions, gathering kernel information, task listing, Detecting hooks, network listing, dumping a file from memory, presenting boot information and lot of other details. This is a must have if the investigation target is a MAC OS X.
18. Chkrootkit
This program is used to determine the presence of rootkits on a system. The program is able to identify the presence of more than 60 rootkits. This will be of great help in analyzing malware infection and cases of network compromise. New rootkits are written to bypass the detection mechanism, but rootkit writing is an art that is tough to master.
19. SIFT
SANS Investigation forensic toolkit is a VM that is preloaded with the tools required to perform forensic analysis. It is perfect for beginners, as it saves- tool finding, downloading and installation time.
Image source: https://www.andreafortuna.org/
20. CAINE
CAINE is an open source Linux distribution that has been developed specifically for digital forensics. It has user-friendly graphical interface and tools. Refer to this link for deeper insight into CAINE: https://www.caine-live.net/

Image source: https://www.caine-live.net/
How does it benefit an organisation and an IT security expert?
Malicious activities happen on a daily basis in organizations. Someone clicked a malicious link, installed a malicious software, visited phishing or malicious websites, etc. It is the responsibility of the investigators to get to the root cause of the issue, and ensure that controls are in place so that the incident does not happen again. A malware incident can bring a company’s network down to the knees and hence an investigation is required. What if an employee resigns from a company or is charged with corporate espionage case. In such cases, organizations need investigators to perform the digital deep dives, to bring out the truth.
It takes time and experience to become an expert in Forensics. The investigator should have critical knowledge about the object being investigated. Any miss in the collection or analysis can have serious impact on the case. Extreme care must be taken by the expert in identifying, preserving and reporting the evidence. Hence, becoming an expert in forensics is not easy, but big bucks are not paid for easy things. This is a niche skill that requires the understanding of each bit of the system, and how to use it as evidence. There are specialized courses in the field as well, if one is interested. Some companies are offering training for their products being used worldwide. One of the products is Encase. The company offers certification for Encase certified Forensic Investigator (also consider checking out this perfect parcel of information for cissp certification).
Conclusion
The article contains some of the popular forensic tools. The tools are not arranged with respect to priority, as they serve different purposes. Some are specifically designed for hard disk analysis, some for mobile investigations and so on. In-case you are new to forensics you can start with individual tools, taking a deep dive into each one. You can also start with the pre-built VM and distributions like CAINE so that you can save time and learn more. Be sure that you relate the information identified with real world scenarios; e.g. infection getting spread via a malicious storage device connected, or a CNC connection created in the networks. You may also search for more forensic tools and experiment. As criminals are getting advanced with each crime; companies are developing more sophisticated tools that can speed up the investigation, if used by experts. The point to be noted here is that, no matter how advanced the tool becomes, it requires an expert eye to identify the logic and correlate the facts.
Click here to jumpstart your CyberSecurity career
