ES5, ES6, ES7, ES8, ES9: What’s new in each Version of JavaScript
Summary
This blog traces JavaScript's evolution, starting from its role in web interactivity alongside HTML to the latest ECMAScript 2018 (ES9) version. Key ES versions are highlighted, featuring ES6's impactful additions like let, const, arrow functions, and promises. Subsequent versions introduced advancements such as the exponentiation operator, async/await, padStart/padEnd methods, and more. This comprehensive overview showcases JavaScript's growth and evolving features.
Table of Content
Javascript is a scripting language introduced to make web pages alive and interactive with the user. The interaction is possible due to the programs or scripts written along with HTML. Javascript was introduced by Brendan Eich, a Netscape employee. Javascript at its development phase was called Mocha and was first shipped with Netscape Navigator 2.0 as LiveScript. Finally, when Netscape Navigator 2.0 Beta 3 was released, it was given the name Javascript. Javascript has come a long way ie from client-side programming/frameworks (like Angular/React) to a server-side technology like NodeJS in 2009.
JavaScript is a key programming language for front-end development. If you are keen on building a career in web development, our Web Development Course is a great choice for you.
What is ES?
In the year 1996, a standards organization called ECMA (European Computer Manufacturers Association) International carved out standard specifications called ECMAScript (ES), which all browser vendors could implement. And Javascript is the most well-known implementation of ES, while ActionScript (from Macromedia/Adobe Systems) and JScript (from Microsoft) are other implementations of ES.
List of Versions from ES
To date, ES has published nine versions, and the latest one (9th version) was published in the year 2018.
- ES1 1997
- ES2 1998
- ES3 1999
- ES4 Abandoned
- ES5 2009
- ES6 2015
- ES7 2016
- ES8 2017
- ES9 2018
ECMA Script's first three versions- ES1, ES2, and ES3 were yearly updates, whereas ES4 was never released due to political disagreements. After a decade, ES5 was eventually released with several additions
ES5
ES5 was released in 2009, ten years after the release of its previous version. Here is a list of features that have come with the es5 version.
1. ‘USE STRICT’ DIRECTIVE:
The earlier versions of JS allow the usage of undeclared variables. But when the es5 ‘use strict’ feature is used, an error is reported.
Ex:
![]()
2. NEW METHODS IN AN ARRAY
- isArray(): This method checks if the object is an array or not and returns the result in true or false.
Ex:

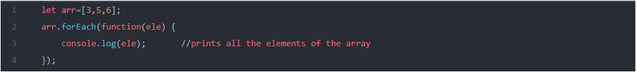
- forEach(): It executes the function for every element found in the array.
Ex:
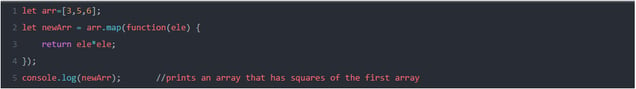
- map(): The map() method creates a new array by mapping every element of the array (on which the map is used).
Ex:
- filter(): It creates a new array that contains elements which got filtered by making array elements pass some condition.
Ex:

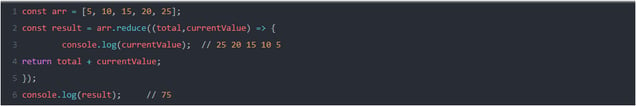
- reduce(): It applies a function to each element in an array and reduces the array to a single element.
Ex:
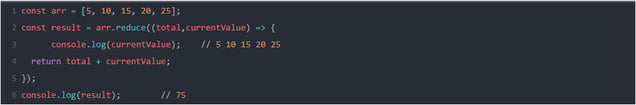
NOTE: This example is the same as iterating over every element to calculate the sum.
- reduceRight(): It is quite same to reduce method, except for the traversal that happens from right to left.
Ex:
- every(): This method checks a condition with every element of an array and if every element satisfies then returns true if at least one element doesn’t satisfy the condition then returns false.
Ex:

- some(): It is same as every() method wherein some() checks for at least one element that gets satisfied with the condition and if found returns true and if none satisfies then false.
Ex:

- indexOf(): Returns the index of the first match in an array. If not found then returns -1.
Ex:
![]()
- lastIndexOf(): Same as indexOf but checks and returns from the other end of an array.
Ex:
![]()
You may also like: Difference Between Java And Javascript
3. JSON SUPPORT
- parse(): It parses a JSON string that is like an object.
Ex:

- stringify(): This method converts an object to a JSON string.
Ex:
![]()
4. NEW METHODS IN A DATE
- now(): The now() method returns the number of milliseconds elapsed since 01-Jan-1970 UTC.
Ex:
![]()
- valueOf(): It returns the primitive value of a date object.
Ex:
![]()
5. GETTERS AND SETTERS:
The get method returns the value of a variable, and the set method sets the value of the variable.
6. PROPERTY METHODS
- Object.defineProperty(): This method lets the user define the property of an object and/or change its value.
ES6
JS has shown great progress in the recent years starting from 2015 by releasing ES6 version. With this release, Javascript has made a big achievement in making a developers life easy and reached the expectations of a modern programming language. Even after 4 years of the release, many newbies to JS are not so familiar with all the versions.
Below is a list of the features that have come with ES6 version:
-
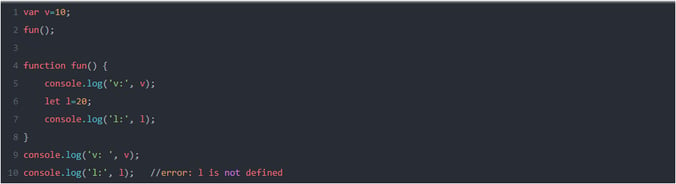
LET & CONST:
Till ES5, JS has only function scope and global scope with the introduction of let keyword in ES6, JS can now have block scope.
Ex:
-
FOR..OF:
for...of is an alternative for both for...in and forEach() and loops iterable data structures like Arrays, Maps, Sets, and strings.
Ex:

-
DEFAULT PARAMETERS:
Provides default values to function parameters if no value or undefined is passed.
Ex:

-
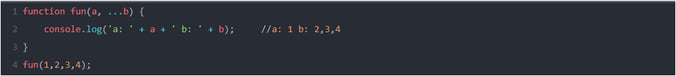
REST OPERATOR:
Rest Operator is used to handle function parameters. It uses three dots as its syntax (i.e …).
Ex:
-
SPREAD OPERATOR:
Spread Operator is used with arrays and its syntax is exactly the same as that of Rest Operator (ie …). It is used to split the contents of an array.
Ex:

-
DESTRUCTURING:
Destructuring helps in unpacking values from an array or an object.
Ex:

-
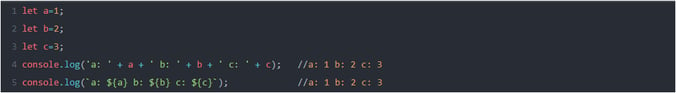
TEMPLATE LITERALS/STRINGS:
It allows embedded expressions, which makes print statements easy.
Ex:
-
ARROW FUNCTIONS:
Arrow Functions use => as its token and so are also called as Fat Arrow Functions. They are one line functions and are much like Lambda functions in programming languages like Java 8 and Python. Prior to =>, JS has a function keyword.
Ex:
![]()
-
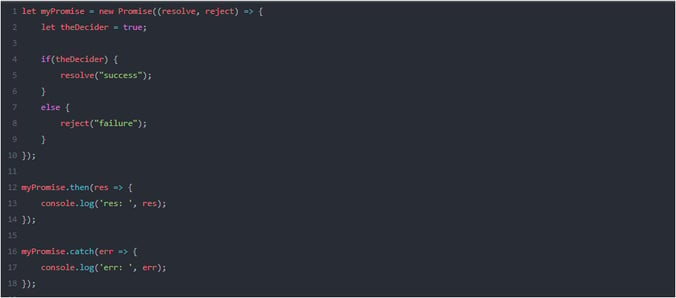
PROMISES:
Promises are introduced in ES6 to handle Asynchronous Programming in a more elegant way. Before Promises, async calls were handled by Callbacks. Promises resolved the Call Back Hell.
Ex:
-
CLASSES:
The Objects in Javascript are based on Prototypes and follows Prototypal Inheritance. But in ES6 the keyword class is introduced that makes the approach very easy.
Ex:

Other features in ES6 include:
- Set, WeakSet, Map, WeakMap
- Generators
- Symbols
- Unicode
- Modules
- Proxies
- Built-Ins
- Binary and Octal
- Reflect
- Tail Call Optimization
ES7
ES7 or ECMAScript 2016 was released in the year 2016. This version gives suitable alternatives to already used functionalities.
-
EXPONENTIATION OPERATOR (**):
ES7 added an exponentiation operator (**) to already JavaScript supported arithmetic operations like +,-,*. This operator raises the first operand to the power second operand.
Ex:
![]()
-
INCLUDES():
Returns true if an array includes a value, if not returns false.
Ex:
![]()
You may also like: Top 51 Javascript Interview Questions and Answers You Must Prepare in 2018
ES8
ES8 or ECMAScript 2017 was released in the year 2017. This version allows new methods of coding with JavaScript.
-
PADSTART():
This method pads a string with another string at the beginning.
Ex:
![]()
-
PADEND():
This method pads a string with another string and makes the resulting string reach a given length. It adds spaces at the end of the string.
Ex:
![]()
-
SYNC/AWAIT:
Await operator, applied only inside an async function, waits to be rejected or resolved by a promise.
-
OBJECT.ENTRIES():
It returns an array that contains the key-value pairs of a given object as an array.
Ex:
![]()
-
TRAILING COMMAS:
A trailing comma is simply a comma that comes at the end of the last item in a list.
Ex:
![]()
-
SHARED MEMORY AND ATOMICS:
The same data can be read and written on multiple threads using the SharedArrayBuffer constructor. Interruption during the process of reading or writing can be avoided by using Atomic objects. This allows the previous operation to finish prior to the next one.
-
OBJECT.GETOWNPROPERTYDESCRIPTORS():
An object is returned to the own property descriptors with get, set, writeable, configurable and enumerable attributes.
Ex:

-
OBJECT.VALUES():
It returns an array of a given object’s own enumerable property values.
Ex:
![]()
ES9
ES9 or ECMAScript 2018 is the latest update and was released in the year 2018.
-
ASYNCHRONOUS ITERATION:
An async iterable object can be used as a loop iteration with the help of for-await-of.
Ex:
![]()
-
REGULAR EXPRESSION IMPROVEMENTS:
A matched object can be returned by using regular expressions of JavaScript. A matched object has array-like value with matched strings.
Ex: to parse a date in YYYY-MM-DD format.

-
REST/SPREAD PROPERTIES:
The last arguments sent to a function are changed to an array using Rest parameters and the (...) notation can be used only for array operations.
Ex:

In an opposite manner, an array is turned into separate arguments using the spread operator. These arguments can be transferred to a function.
Ex:
![]()
-
PROMISE.PROTOTYPE.FINALLY():
The method then() is called after successfully resolving the promise, and the catch() method is declared if a problem occurs. Eventually, the code can be executed using the finally() method, irrespective of previous occurrences.
Conclusion
ECMAScript is a specification, and Javascript is an implementation and implements all the versions that are specified by ECMAScript. And it is one reason why JS is the most popular programming language in the frontend web development. Javascript is everywhere(UI designing/development), backend (server-side coding), mobile applications, game development, etc. It a must for a web developer to update the new versions of ECMA Script and this article is such an attempt.