Lean Six Sigma methodologies: How do they improve Health Care industry?
Introduction:
The need for Lean Six Sigma methods and principles in the healthcare is inevitable. A summary of current studies shows that approximately 30% - 50% of all healthcare works can be deliberated as waste. Wastes in the U.S. health care system cost as much as $700 billion annually. Furthermore, health care faces the slow progression of complex processes. Most of the thehealthcaree practices have not changed in 50 or 60 years.
Health care expenses have been increasing worldwide. This is mostly due to more than normal use of resources. At King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center - Riyadh, Six Sigma DMAIC approach was implemented. This was done to observe more than normal use of the glucose test strips. It resulted in decreasing the needless Quality Control (QC) from 13% to 4%. It reduced the failed QC runs from 14% to 7%. This was done by decreasing the QC to patient testing ratio from 24/76 to 19/81.
Institute Of Medicine report estimates that medical errors cost around $37.6 billion each year. Approximately $17 billion of those costs are linked with preventable errors.
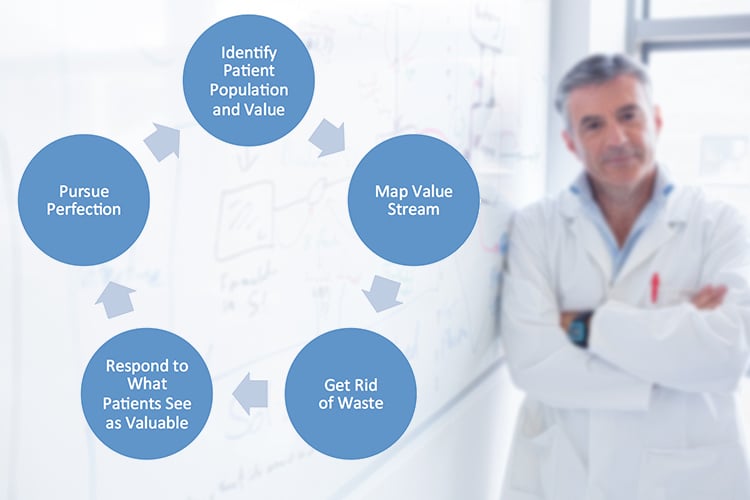
Image source: https://www.ausmed.com/articles/lean-health care
Lean Six Sigma provides proven tools to measure a process and find areas that must be improved. Health care organizations are putting the following to use in these areas of focus:
Discharge and follow up –
Improvements in this area can decrease the number of patients who need readmission to the hospital.
- Emergency department – A positive experience receiving help during worst times of their life can build trust.
- Outpatient services – Patients who have a positive experience with outpatient care are more probable to make use of other medical services.
Thus, with effective six sigma methodologies, patients can assume both better experiences and health outcomes.

Image source: http://www.helpingmakeithappen.com/onlinehealthcareleanbb.html
So, what is Lean?
Lean includes a set of principles, practices and methods for designing and managing processes. Lean is intended to improve efficiency by removing particular kinds of waste. This is also called muda, in Japanese. Muda takes time and resources but does not add any value.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a business management approach used to improve quality and efficiency of any operating process. Six Sigma aims largely to make processes more uniform and precise. It is done through the use of statistical methods. The name Six Sigma refers to a quality level well-defined as the near-perfect defect rate of 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
What are the applications of Lean and Six Sigma to Health Care
Since last 10 years, there have been varieties of health care projects applying Lean and Six Sigma strategies. This lead to health care quality improvement. For e.g., pilot programs applying Lean approaches at Intermountain health care resulted in considerably reduced turnaround time for pathologist reports.
The uses of Lean Six Sigma in health care are profusely clear. Preventing medical errors, decreasing mortality rates, reducing lengths of stay, improving patient care and increasing quality.
The 2017 Health Leaders Media Patient Experience Survey was freshly released. It found that 13% of the health care organizations surveyed said they saw major improvements in patient scores. Another 44% saw moderate, while 30% saw minor improvement.
So, should we prefer Lean or Six Sigma?
Lean works categorically well for health care in large and small organizations. Lean is basically about removing anything that the customer is not willing to pay for.
Highly skilled Six Sigma experts use the steps of the DMAIC model. It is used to develop and design a process, so that there is effectively a one-in-a-million opportunity that an error will occur.
Six Sigma’s applications are most realistic in large organizations. For smaller organizations, the goal of designing defect-free processes to six sigma can be daunting.
Lean work is rigorous. Collecting and measuring data is a crucial part of the lean process but the work is not aligned on a time-consuming process of collecting and analyzing statistics.
Leaders, suppliers and staff work together to improve processes incrementally for the patient with Lean. The goal is to achieve zero defects in all their improvement work.
Pic Ref: https://in.pinterest.com/pin/847802698572484341/
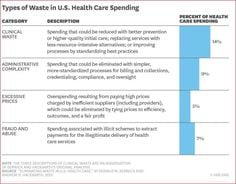
Waste in health care:
Nobody likes waste. If an action wastes our money, we drop it from our schedule.
The three types of waste in health care—administrative, operational, and clinical. Both administrative and operational waste are constituents of inefficient production. Clinical waste is a type of allocative waste.
- Administrative waste is the excess administrative overhead.
- Operational waste denotes to other aspects of inefficient production processes.
- Clinical waste is waste created by the production of low-value productions.
Estimates of Wasted Clinical Spending in the United States:
| Clinical Service | Total Annual Dollars ($ in Millions) Wasted | % of U.S. Health Care Spending |
| Excessive antibiotic use for viral upper respiratory infections and otitis media | $525–$546 | 0.03 |
| Avoidable emergency department use | $3,000 (upper bound) | 0.16 |
| Avoidable hospitalizations of nursing-home patients | $7,500 (upper bound) | 0.4 |
| Overuse of cytology for cervical cancer screening | $630 –$4,000 | 0.03–0.21 |
| Inappropriate hysterectomies | $1,119 | 0.06 |
| Needless hospital admissions for chest pain | $4,443 | 0.23 |
| Overuse of noninvasive radiologic imaging | $18,210–$33,333 | 0.96–1.75 |
| Inappropriate spinal-fusion surgeries | $11,118 | 0.59 |
| Total | $36,044–$65,099 | 1.90–3.42 |
Table ref: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2690367/table/tbl6/
The following compelling statistics prove the need to cut health care costs. Average health care expenses per capita go beyond $8,000 in USA
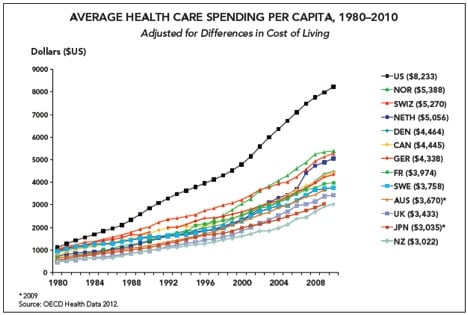
Image source: https://www.healthcatalyst.com/health care-analytics-reduce-costs
As demonstrated by this chart, much of that cost is being moved into high-deductible health plans.
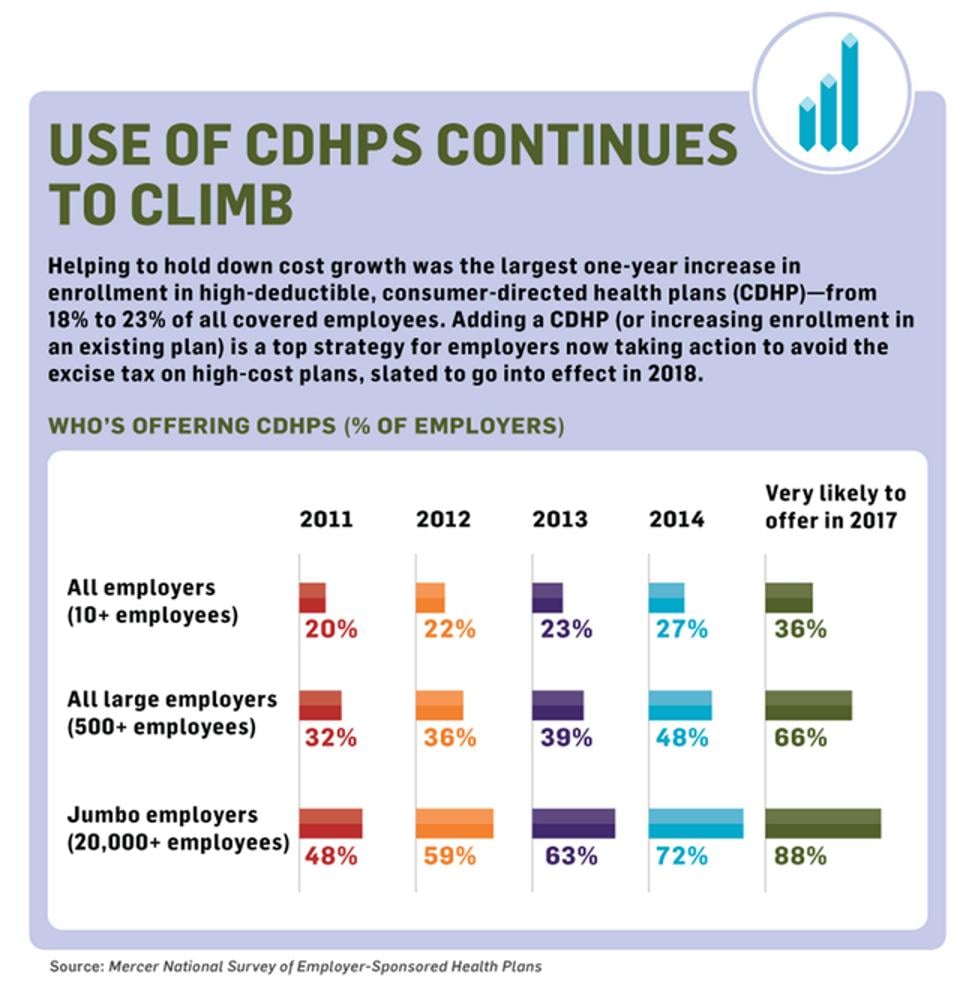
Image source: https://www.forbes.com/sites/danmunro/2015/01/04/u-s-health care-spending-on-track-to-hit-10000-per-person-this-year
United States implemented all the methods, whose effectiveness was measured. Only 40% of the projected $1 trillion of wasteful spending was treated. It left an ample opportunity for innovation in all other areas of health care.
Lean will help generate further savings by decreasing waste, decreasing medical errors and refining quality. It will also help in improving patient report conclusions and recognizing, preventing, and managing prolonged disease.
The breakup of the $147.7 billion allocated for health care initiatives is:
- $24.7 billion to provide a 65% subsidy of health care insurance premiums for jobless
- $86.6 billion for Medicaid
- $19 billion for health information technology
- $10 billion for health research and construction of National Institutes of Health facilities
- $1.3 billion for medical care for service members and their families (military)
- $1 billion for prevention and wellness
- $1 billion for the Veterans Health Administration
- $2 billion for Community Health Centers
- $1.1 billion to research the effectiveness of certain health care treatments
- $500 million to train health care personnel
- $500 million for health care services on Indian reservations
Case Studies:
Using DMAIC to Improve Nursing Shift-Change Assignments: In this case study of a hospital, master of advanced nursing passed nursing department leaders wanted to improve the efficiency of their staff’s shift change tasks. Upon value stream mapping the process, team members recognized the shift nursing report clocked 43 minutes on average to complete. Using DMAIC and other quality tools, team members improved the process’ sigma level from 0.7 to 3.3.
Reference: http://asq.org/knowledge-center/case-studies-dmaic-improve-nursing-shift-change.html
Examples of Clinical Six Sigma Projects:
The following proposes a brief look at project focusing patient safety, medical error reduction, clinical process improvement, patient satisfaction and outcomes.
- Project: Defining ‘Captain of the Ship’ to Raise Quality and Patient Satisfaction’
Provider: Charleston Area Medical Center
Project Goal:
- Make sure there is a physician identified to manage each patient’s care
- Improve patient and family satisfaction about communication and coordination of patient care
- Project Scoping Finds:
- Need to redesign the care coordination process. This must be done to encourage the right care in the right setting and as a result reduce losses
- Improve non-progressive End of Life Care
- Solutions:
- Revised medical staff rules and regulations about the role of the attending and consulting physicians
- Established pre-scheduled conferences to clarify “Who is in Charge”
- Improved process in identifying the patient’s Advanced Medical Directives
- Results:
- Improved patient satisfaction and quality of care
- Total savings from Captain of the Ship Project: $790,000
- Patient Satisfaction: $240,000
- Care Coordination: $190,000
- End of Life Care: $360,000
Reference: https://www.isixsigma.com/new-to-six-sigma/dmaic/using-six-sigma-improve-clinical-quality-and-outcomes/
The Effects of Six Sigma in healthcare
Here are many healthcare organizations that have successfully implemented Six Sigma as a part of their quality improvement efforts:
- Mount Carmel Health System: Two years of Six Sigma projects dedicated to operational issues and business management helped save the healthcare organization $3.1 million. Employee and physician satisfaction rates also improved.
- Boston Medical Center: An emphasis on diagnostic imaging was laid. That brought cost savings and revenue rises of more than $2.2 million.
- Rapides Regional Medical Center: This healthcare organization used Six Sigma method to reduce defects in its emergency department. Wait times dropped. Providers saw more patients. The hospital saved more than $950,000 annually.
- The Women and Infants Hospital, Rhode Island: The hospital effectively executed Six Sigma to systematize its processes for embryo transfer. This lead to raise execution rates by 35%.
- Valley Baptist Health System: They reduced surgery cycle time using Six Sigma method. This helped the hospital to add adequate capacity to handle 1,100 more cases per year. This increased potential annual income by $1.3 million.
- Yale-New Haven Medical Center: Many Six Sigma projects implemented in the surgical intensive care unit. This lead to a 75% reduction in bloodstream infections. This also resulted in an estimated $1.2 million in annual savings.
Pursuing tangible opportunities (e.g., reducing administrative complexity) would yield $130 billion. The United States could save a total of $440 billion per year. This is equal to 14% of total spending on health care. If realized over five years, this would halve the expected growth in health care spending. Reducing the average annual growth rate from 5.5% to 2.4%.
Conclusion:
Six Sigma and Lean combined, is a well-managed process. These managed processes are for methodically scheduling and executing innovation projects. Such projects can be educated, learned, and imparted with a high degree of success. Lean and Six Sigma have immense complementary strengths. Six Sigma with Lean tools and best practices, give solutions for problems such as waste and time consumption.
Health care leaders have to deal with rising costs in health care, so that a higher proportion of the citizens is able to pay for high-quality health care. If health care services are inefficient, they cost more. Because of this, fewer can get profit from the technical advances of modern medicine. Industrialization of services improves quality while making those services further cost efficient.
REGISTER NOW to learn more about Lean Six Sigma Applications
