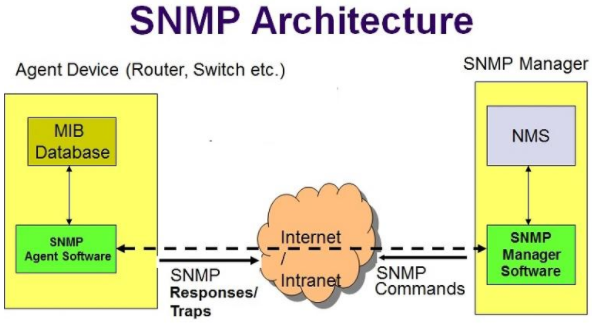
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is an application layer protocol which uses UDP protocol to maintain and manage routers, hubs and switches other network devices on an IP network. SNMP is a very common protocol found enabled on a variety of operating systems like Windows Server, Linux & UNIX servers as well as network devices like routers, switches etc. SNMP enumeration is used to enumerate user accounts, passwords, groups, system names, devices on a target system. It consists of three major components: Managed Device: A managed device is a device or a host (technically known as a node) which has the SNMP service enabled. These devices could be routers, switches, hubs, bridges, computers etc. Agent: An agent can be thought of as a piece of software that runs on a managed device. Its primary job is to convert the information into SNMP compatible format for the smooth management of the network using SNMP protocol. Network Management System (NMS): These are the software systems that are used for monitoring of the network devices. An agent running on every SNMP device will be providing access to a read and writable database. The database is referred to as the management information base (MIB) which is organized hierarchically and is a virtual database containing a formal description of all the network objects identified by a specific object identifier (OID) that can be managed using SNMP. It's a giant repository of values and settings. There is a manager involved in the process, and the manager will query the agent for various details. Community strings is a text string used to authenticate communications between the management stations and network devices on which SNMP agents are hosted. Community Strings travel in clear text over the network, hence are subject to network sniffing attacks. Community Strings are sent with every network packet exchanged between the node and management station. Two types of community strings: Read only: This mode permits querying the device and reading the information, but does not permit any kind of changes to the configuration. The default community string for this mode is “public.” Read Write: In this mode, changes to the device are permitted; hence if one connects with this community string, we can even modify the remote device ’s configurations. The default community string for this mode is “private.” when the community strings are left at the default settings, attackers take the opportunity and find the loopholes in it. OpUtils Network Monitoring Toolset - http://www.manageengine.com SolarWinds ( best SNMP enumeration tool) - www.solarwinds.com command line tools: SNMP-WALK, SNMP-CHECK Remove or disable SNMP agents on hosts Block port 161 at all perimeter network access devices Restrict access to specific IP addresses Use SNMPv3 (more secure) Implement the Group Policy security option called "Additional restrictions for anonymous connections" Access to null session pipes, null session shares, and IPsec filtering should also be restricted
SNMP Enumeration
Few tools:
Countermeasures: