Evolution of ITIL 4 and its dimensions
ITIL is an acronym for Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It is described as “Good Practices of the framework” for IT services.
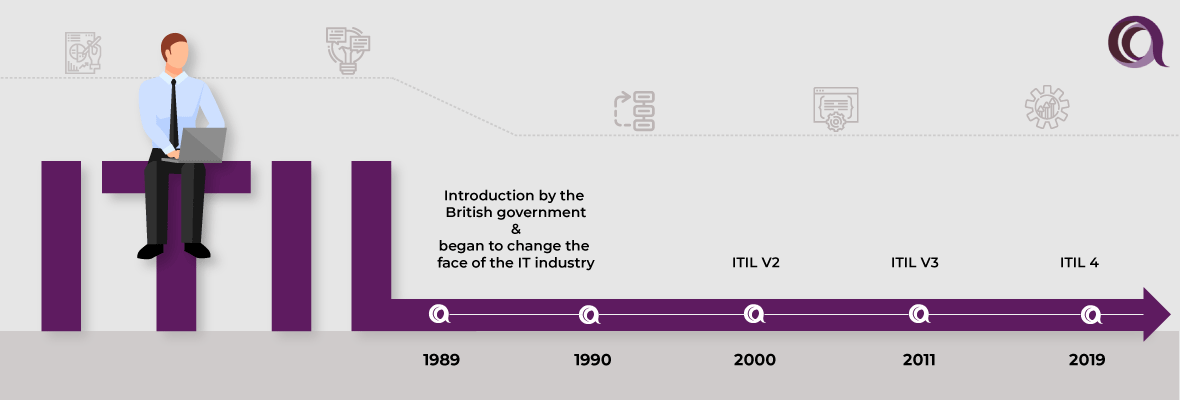
It was first introduced in 1989 by the British government. ITIL came from the Office of Government Commerce (OGC). In the early 1990s, ITIL began to change the face of the IT industry, not just in the UK but all around the world.
How ITIL Evolved Until Date
In the year 2000, ITIL V2 came to market. And ITIL developed standardized methods for best practices in the IT industry.
ITIL V2 had only two main processes.
1. Service Support, and
2. Service delivery.
In the year 2011, ITIL V3 was released and consisted of five stages. Each of these five stages focused on a specific service lifecycle.
The knowledge of ITIL helps us
1. Reduce costs,
2. Build more efficient IT frameworks, and
3. Provide the best services possible in the IT industry
Most companies are adopting ITIL standards in their projects.
In 2019 ITIL 4 was released, and it remains the latest version of ITIL. IT management was the focus area of improvement in ITIL 4.
This latest ITIL update is a response to the technological, organizational, structural, and other shifts in the IT space. Most companies are struggling to keep up with these advancements. Hence, ITIL 4 becomes necessary to address these shifts.
ITIL 4 enhanced its standards. So it’s become the standard best practice framework. It supports organizations going through changes.
The advancements in ITIL 4 positions it well to deliver value, faster for individual users and organizations.
Information: Facts about things
Technology: Invention of tools to ease in our daily lives
Infrastructure: IT services
Library: Collections of data, knowledge, and intelligence
Advantages Of ITIL Standards in the IT Industry
What makes ITIL standards win admiration across the IT industry?
● Saves time and improves service delivery: ITIL standards significantly lower issue resolution time. This time saving improves IT services delivery and client satisfaction.
● It’s accepted globally: A global procedure that is maintained by all organizations to improve IT quality services.
● Manage Business Impact: ITIL standards help the service desk team. They can proactively reduce any unwanted business impact due to IT management issues.
● Incidence Management: Incident management is a vital part of the ITIL process.
● Grant Entry into IT: ITIL knowledge empowers people from any domain to enter into the IT industry with minimal resistance
ITIL Dimensions
ITIL consists of five dimensions or stages targeted at providing improved service quality in the IT industry. These dimensions subdivide into 26 processes and four functions.
Each of the five stages concentrates on a specific phase of the service lifecycle. These five dimensions give users the freedom to create their standard operating procedure. So they can provide top-notch IT services.
The strategy stage is the first step in the ITIL process.
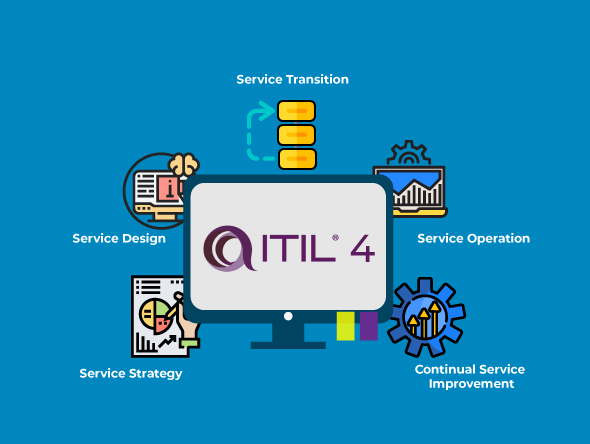
Service Strategy
The Service Strategy stage focuses on strategy design and development. This stage aims to meet customer requirements for services management.
Users prioritize their service delivery at this stage. Especially when they’re just starting with ITIL. But this Service Strategy stage can also be used to improve on an existing service or to create a new service from scratch.
Service Design
The Service Design stage uses the developments from the Service Strategy stage to build a design process. The knowledge of service design benefits the pre-sales team. Managers and business leaders benefits by addressing their clients’ concerns more efficiently.
Service Transition
Service Transition gives guidance for moving the developed and changed services into operations.
Service Operation
Now, Service Transition guides moving developed and changed services into operations.
Continual Service Improvement
The Service Improvement stage provides direction to improve on existing or new IT services. Service Improvement recommends points of improvement in all phases of the project lifecycle.
This stage proffers improvements. It monitors and measures values like Process Compliance, Quality, and Performance.
Important ITIL Processes and Functions
Let’s explore the core ITIL processes and their functions.
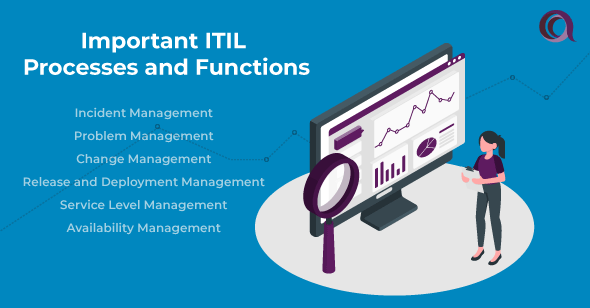
Incident Management
Any service degradation in IT service is an “Incident.” Incident management is prompt service restoration. But must come with little or no impact on business operations.
We have five types of incidents: P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5.
Priority = Impact + Urgency
The incident management process ensures the expected service quality is achieved and delivered.
Problem Management
A problem is an unknown cause of one or more incidents. And the prevention of a problem or incident is problem management.
You’ll need to perform a root cause analysis (RCA) to understand the root cause of a problem before you can resolve it.
This process improves service availability and the quality of IT services that ITIL users deliver.
Change Management
This process is for making enhancement or changes in service operations. Changes are recorded, planned, designed, tested, and first implemented in the lower environment. And then if they work as expected, the changes get moved to service operations.
But, it’s best practice that before making any changes in service operations, you ensure there is a rollback plan.
Each change must be recorded and must be approved by authorized people. These authorized persons would be either of these people:
CAB – Change Advisory Board
ECAB – Emergency Change Advisory Board
Release and Deployment Management
This process ensures that the required changes get tested and deployed in a lower environment first. And then if they work as expected, these changes get moved to service operations.
Access Management
This process controls access to applications. Authorized users gain access to applications, and unauthorized users are denied access. This function ensures that only authorized users can access services.
Service Level Management
Service Level Management ensures the timely delivery of all IT services.
Availability Management
To ensure that the availability of services is delivered in all the services as per the agreed timeline.
ITIL Functions
Service Desk: This team is responsible for restoring service to users as quickly as possible, in the event of a service failure.
IT Operations Management: This caters to the daily operational activities. Especially activities needed to manage and maintain an organization’s IT infrastructure.
Things To Know and Remember in ITIL 4
Known error: A problem that’s been analyzed and has a workaround, but has not been resolved permanently.
Problem: Unknown cause of one or more incidents
SOR: Service Outage Report
Alert: Warning of reaching threshold frequency.
Incident management: Restore of service normal in the shortest time possible. And with minimal business impact.
SLA: Means Service Level Agreement. It’s an agreement between a customer and a service provider.
OLA: Is Operational Level Agreement, which is an agreement between a service provider and internal teams.
UPC: Stands for Underpinning Contract. This agreement holds between a service provider and a vendor.
Priority: Defined as P = Impact + Urgency
Service Request: This is a user request for accessing new applications.
Change: Removal, addition, or modification of any item is change.
Normal Change: This is a change that follows all the steps outlined in a change management process.
Emergency Change: This is the change that requires prompt approval. So it must follow a different procedure in the change management process.
Deployment: Means testing and implementing required changes in lower environments or production.
Key Performance Indicator: Metric for measuring improvements and performance when managing IT services.
Service: Means delivering value to customers or meeting customer requirements.
Major Incident Management plays a vital role
P1/P2 incidents are major incidents.
If an issue impacts production and affects most users, it comes under P1/P2. Major incidents have unique procedures for handling them.
Using the standard operating procedures (SOP) of ITIL, we can handle, resolve, and reduce major incidents.
Priority = Impact + Urgency
How to move from operations to IT with ITIL knowledge
ITIL has its standards and procedures for providing improved IT services. Your background doesn’t count if you decide to acquire knowledge of ITIL and earn a certification in it.
You’d stand a better chance of gaining internal opportunities within your organization. You’d be a step ahead of others who do not have ITIL knowledge and certification.
ITIL help’s PMO Role
Learning ITIL benefits IT professionals and others.
Business leaders and management personnel gain the ability to address customer concerns better.
PMOs that have ITIL knowledge give their company an edge. They solve problems proactively and approach their business and clients better. ITIL knowledge also helps with understanding product quality.
ITIL certification is mandatory for IT jobs
Nowadays, we see most companies seeking ITIL certified candidates.
The ITIL scheme has five certification levels.
1. Foundation
2. Practitioner
3. Intermediate
4. Expert
5. Master
To register or to complete your training in the ITIL certification program, please click on the link below.
https://www.greycampus.com/workshops
Looking for an ITIL Certification course? Click here to know more!