ITIL 4: The 10 major updates in the current version
This post describes the changes associated with upgrading ITIL V3 to ITIL 4. You'll discover the ten key changes and upgrades across the ITIL framework.
Let's have a look.
1. The move from Processes to Practices
ITIL 4 introduces practices instead of processes; the service delivery of ITIL V3 was upgraded to deliver more value in ITIL 4. You'll find these practices under the general service and technical management. These upgrades make the new framework flexible and future-ready.
More so, these improvements are beneficial for adapting to the digital era. Hence, the changes in the processes of ITIL V3 lifecycle to practices, principles, and concepts in ITIL 4.
See the differences in the table of comparisons below.
.jpg)
Image source: YaSM
2. A Holistic Approach
ITIL 4 defines four dimensions that are considered as a holistic approach to service management:
1. Organizations and people,
2. Information and technology,
3. Partners and suppliers,
4. Value streams and processes.
ITIL V3 defines the systematic approach rather than the holistic approach that involves these four dimensions. Whereas the ITIL 4 service value chain uses these dimensions to bind the whole flow in the new framework. Specifically, the ITIL V3 focuses on individual processes.
3. Service Value Chain from Service Lifecycle
The Service Value System (SVS) promotes business strategies that result in mutually beneficial outcomes. In this system, all the components and activities of an organization work together to enable value creation. The SVS co-creates with organizations, their customers, and stakeholders to support an ecosystem of value delivery for all parties involved.
Let’s look at how SVS supports this value chain under six activities.
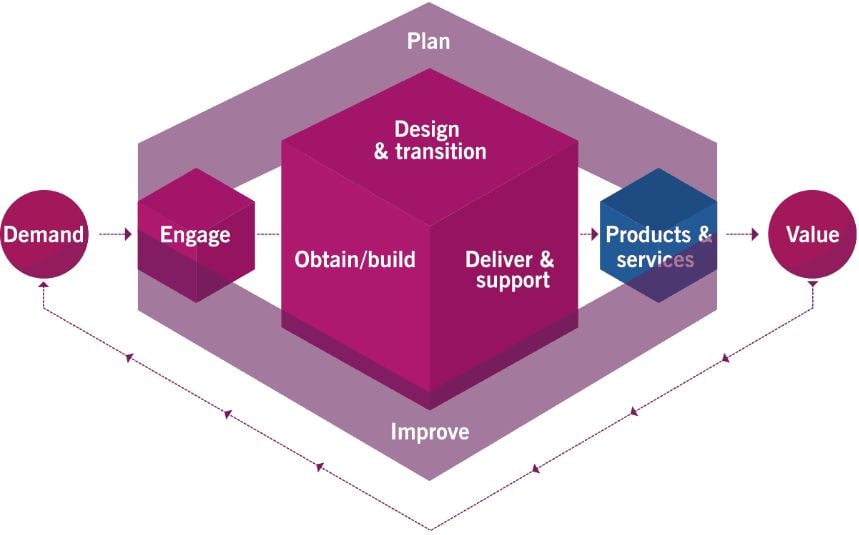
Image source: AXELOS, "ITIL Foundation: ITIL 4 Edition" (2019)
Engage: This activity involves the engagement of suppliers or partners for service delivery.
Plan: Plan covers planning and estimating the availability of resources for service delivery and the requirements for the future.
Improve: Improve where necessary as there is always room to enhance the user experience.
Design and Transition: The activities here revolve around deciding the products and services to build. It also involves making sure the products and services created fits their purpose of use.
You’d need to also decide on how to deliver them to the market. So, while at the design phase, keep these points in mind.
Obtain or Build: This activity makes sure that service components are available when you need them. This step would take inputs from
> The architectures or policies for the organization,
> Engagement of suppliers and partners, and
>The outcome of the design phase
All these activities are interrelated.
ITIL V3 also describes the 26 processes under the Service Lifecycle, but the SVS has a more holistic approach. Organizations can implement SVS based on their demands.
4. Prominent changes in CSI approach
The lowest block in the service value system is Continual Service Improvement (CSI). CSI is the response effort to the changing needs of products or services management.
The CSI model has improved in ITIL 4. This advancement rides on the premise that there is always room for improvement. Just as the title "CSI" suggests, improvement is continuous, and it never stops.
The top leaders in any organization are involved in forming the organization’s vision. These executives must work with CSI. So, the continual improvement model incorporates the seven guiding principles, which are based on Agile, DevOps, and Lean methodologies. Hence, it covers a more extensive area apart from services in IT.
5. Enabling co-creation of value
ITIL 4 supports and enables value co-creation by facilitating outcomes that customers want to achieve. This feature is an added advantage to the customers because they don’t have to manage specific costs and risks. So the change isn’t only from delivering value but also to co-create with the customers as well.
6. Change in the Guiding Principles of ITIL
The nine guiding principles for ITIL practitioners have been compressed to seven in ITIL 4. Now, you can use these principles holistically, and they are more practical to apply.
The seven ITIL guiding principles are:
1. Focus on value
2. Start where you are
3. Progress iteratively with feedback
4. Collaborate and promote visibility
5. Think and work holistically
6. Keep it simple and practical
7. Optimize and automate
Although you can’t find these principles in ITIL V3 publications, they’ve been covered in the nine guiding principles of ITIL V3.
7. The Practices in ITIL 4
ITIL 4 has more practices than the processes in ITIL V3. It has 34 practices with a similar baseline to the V3 concept. These practices are categorized into three, as you’ll see below.
General Management Practices
- Architecture management
- Continual improvement
- Information security management
- Knowledge management
- Measurement and reporting
- Organizational change management
- Portfolio management
- Project management
- Relationship management
- Risk management
- Service financial management
- Strategy management
- Supplier management
- Workforce and talent management
Service Management Practices
- Availability management
- Service validation and testing
- Business analysis
- Service design
- IT asset management
- Service configuration management
- Monitoring and event management
- Service level management
- Release management
- Service catalog management
- Incident management
- Service continuity management
- Capacity and performance management
- Service desk
- Problem management
- Service request management
Technical Management Practices
- Deployment management
- Infrastructure and platform management
- Software development and management
8. ITIL 4 gives Governance Autonomy
The governance component of ITIL 4 in the service value system is about the control and direction of an organization.
In ITIL V3, Service Strategy covered governance. However, the new framework helps to put a clear picture of the governance model. The upcoming modules would publish these changes.
9. Introduces new Software Development and Management Approach
ITIL 4 provides a high-level overview of software development and management activities. While ITIL V3 describes a similar concept in the Application Management function of the ITIL Service Operation publication.
10. Built with automation in mind
The ITIL 4 approach covers the technologies under industrial revolution 4. Robotics, AI, nanotechnology, IoT, automation, quantum computing, biotechnology, etc.
Due to digitization, the complexity has increased, and ITIL 4 will help organizations adapt. It has a future-proof approach to business as it addresses the digital approach to optimization and automation.
Upskill to ITIL 4. Take the course now!