21 Project Management Buzzwords to Learn With A PMP Bootcamp
How indispensable is project management to an organization? While some believe it is a needless burden and a financial liability, good project management is the glue that holds the project team and clients together. It is all about going out of your way to build a vision for projects and keeping team members on the same page to get things done.
To speak the same language as your team members and to stay up to date in your industry, an aspiring project manager needs to be familiar with popular project management buzzwords.
Top 21 Project Management Buzzwords to Learn in 2021
Here are the top 21 buzzwords that you must know in 2021.
1) Arrow Diagramming Method (ADM)
The Arrow Diagramming Method is a schedule network diagramming method used in project management. This method acts as a tool to ensure tasks are completed on time and resources are used correctly.
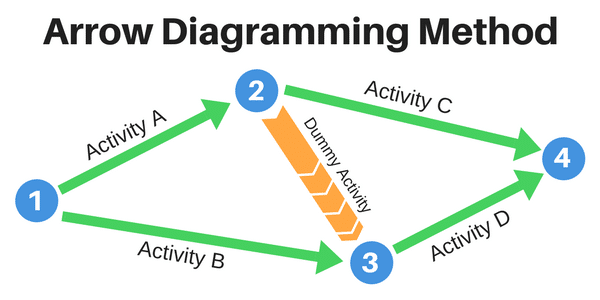
Source: Workzone
How are arrows used in this method?
- The base of an arrow represents the beginning of each activity.
- The pointed end represents the end of a schedule activity.
- The length of the arrow represents the timeframe.
- The activities are connected at various points called nodes.
2) Scope Creep
No matter how simple or complex the project is, defining the scope is of paramount importance in project management. Scope creep or feature creep in project management refers to the way the requirements of a project tend to build over time. For instance, a project that aimed to release one deliverable may end up releasing three more deliverables.
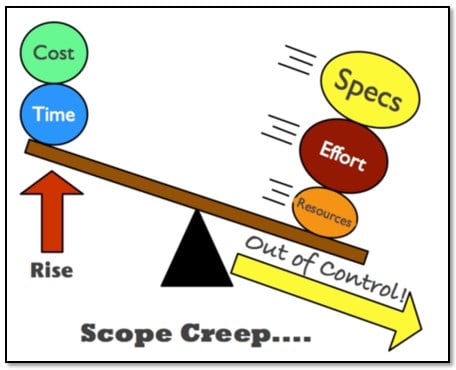
Source: Medium
The major causes attributed to the development of scope creep include changing requirements of stakeholders, and evolving customer needs and market trends. Scope creep can be effectively managed by closely monitoring the status of the project and comparing work performed against baseline requirements. Analyzing changes, their causes, and severity are also critical in tackling scope creep.
3) Mission Critical
Mission critical in project management refers to a system, software, process, or procedure that when it fails could derail the entire project. In essence, mission critical is inevitable for the progress of a project; it needs to uninterruptedly assist the processes and practices involved. The failure of a mission critical service can cause disruption of services and financial challenges. A SaaS (software as a service) system, a Distributed Control System, a transactional monitor with high performance, a system that controls equipment in hospitals such as ultrasound devices, and a system that accounting and billing calls on phones are some of examples of mission critical.
4) Sprint
Source: Asana
A sprint refers to a short, scheduled period of time during which a project management team accomplishes a certain task assigned to them. It is a repeatable cycle of work bound by time. It is used in software development to implement agility and flexibility. Sprints help a development team adapt to changes. Using sprints, a complex project is broken down into individual bite-sized tasks. They last less than a month and are enhanced by rigorous feedback cycles. The shorter the span of the sprint, the faster the delivery of feedback.
5) Process Improvement
In a nutshell, project management is a combination of simple and complex processes. These processes are indispensable in creating a final product that delivers the promised value. Process improvement is the practice of identifying and improving processes that need to be optimized to improve quality or to meet customer demands. This activity is crucial to minimize error and waste and to maximize productivity.
Process improvement typically involves a systematic methodology. It is a proactive attempt to maximize the quality of the product by spotting processes that have room for improvement. Process improvement spans project duration.
6) Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart is one of the most popular project management buzzwords. It is a table used in project management to represent the entire course of a project and all the elements involved. It reveals all upcoming deadlines and tasks on a timeline. It can be used to view the entire landscape of one or more projects. Gantt charts help you tackle the practical aspects of your project.
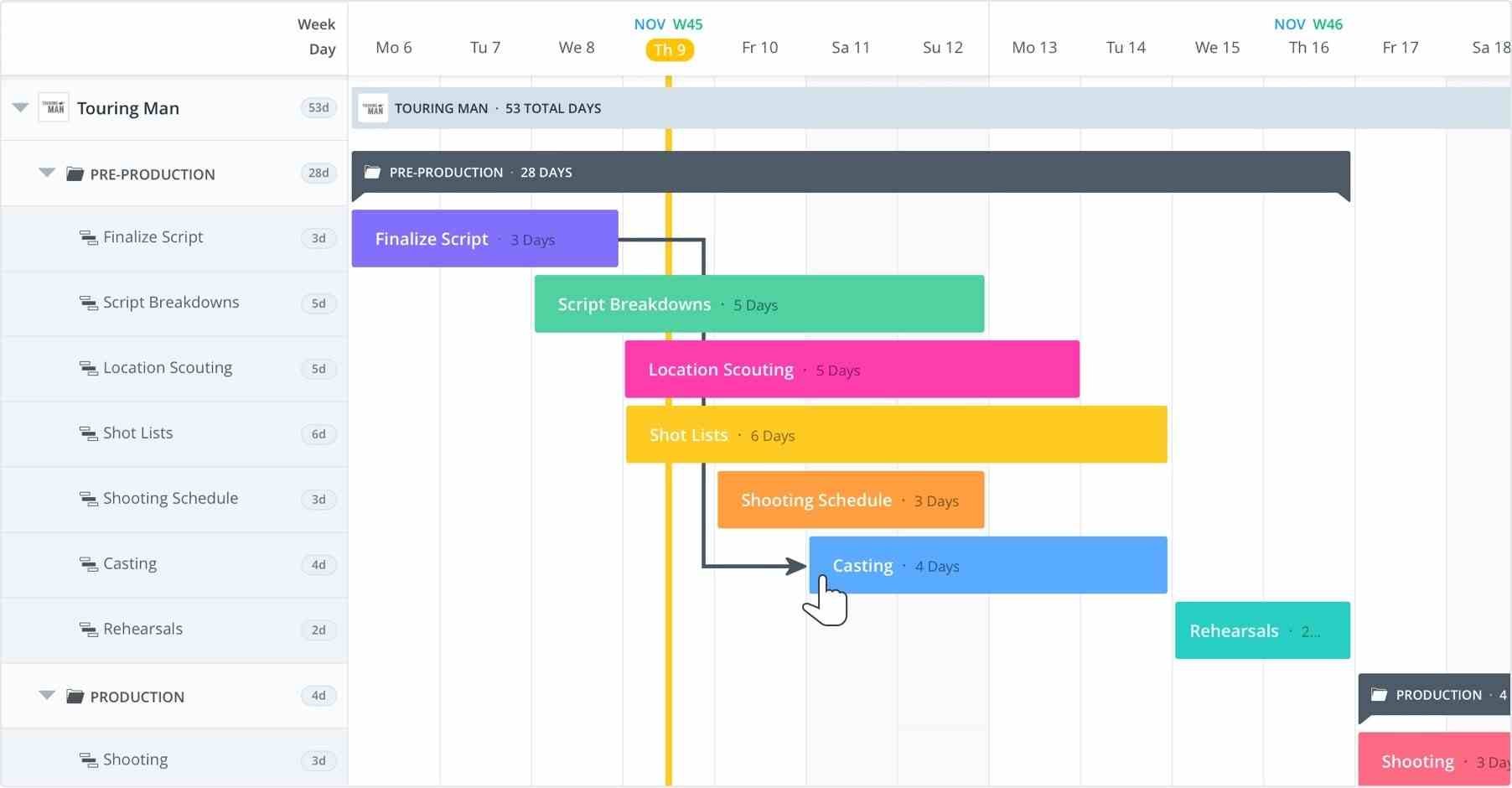
Source: ClickUp
What elements are represented in Gantt charts?
- The date of project initiation
- The list of tasks
- Who handles a task
- The start and end dates of each task
- How tasks interconnect, overlap, and group together
- The project end date
7) Milestone
A milestone refers to points in the lifecycle of a project where progress is measured. They act as signal posts for the commencement and conclusion of a project, reviews, submission dates of deliverables, budget checks, and more. Project milestones need to be simple; they could be as undemanding as scheduling a meeting with stakeholders. The simplest method to visualize milestones is to use a Gantt chart, which allows a one-glance status check of all tasks.
8) Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
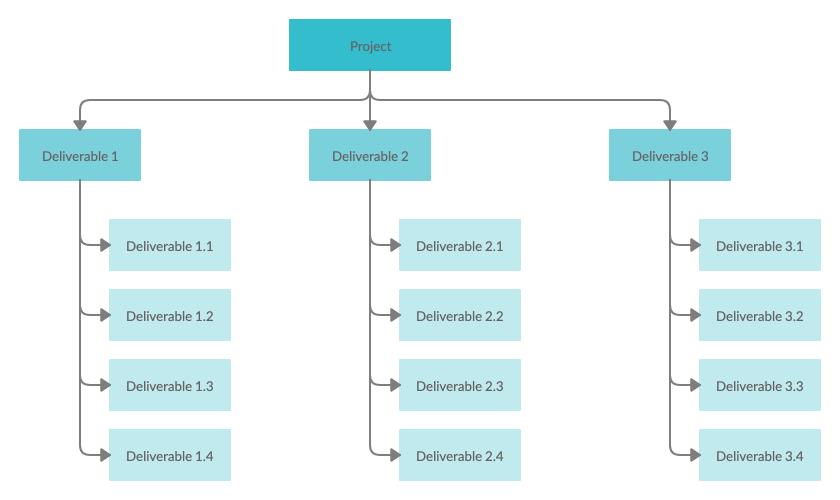
Source: Creately
A work breakdown structure is an approach used in project management to complete complex projects. The ultimate goal of employing this method is to simplify a multi-step project and make it more manageable. The project is broken down into multiple chunks and delegated to different teams; this way, things can be completed faster and more efficiently.
How is a WBS created? To use this method, the scope of the project needs to be defined first. All crucial inputs are gathered and transparently represented. Task priorities are established as well as task connections. Tasks are then assigned to different teams who are expected to complete them within the given constraints.
9) Baseline
A project baseline is a defined starting point in a project plan. It acts as a reference point for measuring your project’s progress. A project and its control activities are initiated only after defining and documenting the baseline. A project baseline is created by first defining the scope of the project. Its schedule is then mapped out, and the total cost is estimated. Once the execution commences, the project baseline is pushed to change control.
Accurate measurements can only be made if the scope, schedule, and cost are under flexible change control disciplines. If a change is approved, the baseline is redefined to accommodate the new change along with the original project plan. This makes baseline a timeline of all the changes in a project plan.
10) Synergy
When two or more organizations join forces to deliver a combined effect that is greater than the impact these entities can produce individually. The idea of synergy is grounded in successful symbiotic relationships where two groups complement each other. Synergy is an inclusive approach in project management as it brings together people from diverse backgrounds and locations. It not only generates better solutions to problems but also paves the way for positive evolution.
11) Triple Constraints
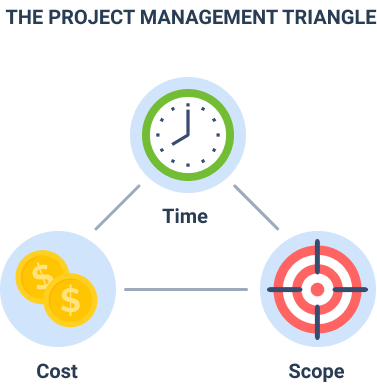
Source: actiTIME
Every project is executed within three constraints: scope, cost, and time. These factors are collectively referred to as ‘the triple constraint’ in project management. The triple constraint is often represented using a triangle with quality as the central theme, where each vertex of the triangle is formed by a constraint.
Now how do you execute the project management triangle?
- Communicate the scope clearly to the team. Make sure you are transparent and that you convey all details of the project to your team members.
- Establish and track deadlines. Monitor your schedule; add milestones to emphasize important deliverables and dates. Use baselines effectively to track your progress.
- Monitor the cost of your resources. It goes without saying that time is money in any project plan. It is important to leverage time tracking tools to track your expenditure. This allows you to keep your budget on track.
12) Due Diligence
Due diligence is a term used in association with risk management. With due diligence, you attain a better understanding of potential risks, failures, issues, and opportunities. It lets you establish mitigation strategies and gives you a clear picture of all the ‘what if’ scenarios. A project manager executes due diligence by setting clear objectives and assessing the strength of individuals and resources. Armed with this knowledge, a project manager can approximate the risks a project might incur.
13) Project Life Cycle
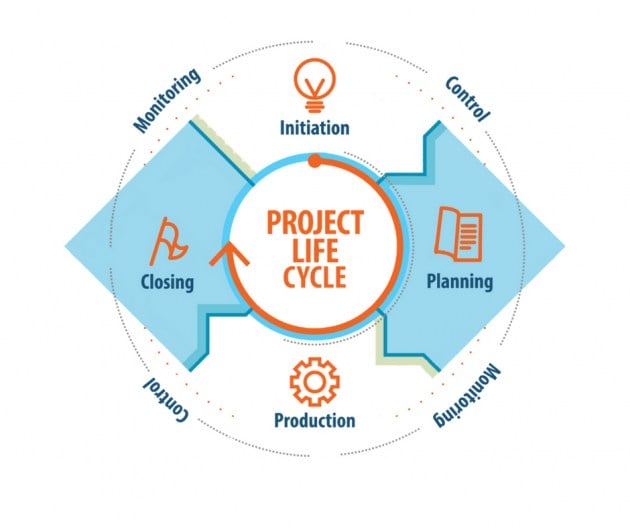
Source: twproject
The sequence of stages that a project moves through from the point of initiation to closure is called its lifecycle. A project lifecycle is influenced by critical factors, such as management decisions, the nature of the project, and its applications.
The following are phases in a project lifecycle:
- The Initiation Phase ─ This is where the scope of the project is defined. The information generated in the process is then used to create a project charter.
- The Planning Phase ─ This is where all the strategies pertaining to the project are laid out about project execution.
- The Execution Phase ─ This phase is marked by the implementation of activities and decisions planned in the planning phase.
- Monitoring and Controlling ─ All processes are closely monitored and controlled in this stage.
- The Closure Phase ─ This phase is where a project is officially closed.
14) Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation is one of the most critical project management buzzwords. It refers to the combination of measures adopted by a project manager to eliminate or minimize project risks. There are multiple risk types, such as monetary risks, technical risks, and schedule-based risks. It is the authority of the project manager to minimize project risks. Usual risk mitigation routines include classifying risks based on their nature and priority. Once their priorities are established, the project manager can tackle them in a sequential manner.
15) Contingency Plan
A contingency plan is an actionable plan implemented if a predicted risk becomes a reality. It explains the measures to be taken after an identified risk occurs. These plans are devised only for identified risks, not unknown risks.
How to create an effective contingency plan?
- Identify what might demand a contingency plan
- Identify the 4Ws and 1H ─ who will be involved, what do they do, when does it happen, and how does it happen
- Set plans for communication
- Track the plan consistently
16) Critical Path Method (CPM)
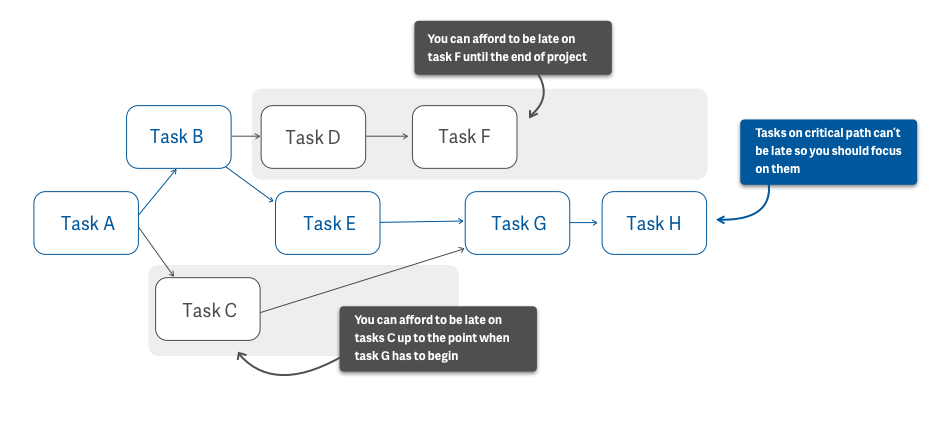
Source: ActiveCollab
The critical path method (CPM) refers to the longest sequence of activities or tasks to be completed within the entire duration of the project. These tasks are inevitable for successful project completion. Each task in CPM is called a critical activity; a delay in executing a critical activity will delay the entire project. That is, you can establish the total duration of the project by identifying your critical path.
A critical path is calculated during the planning phase to determine important activities and deadlines. Once the critical path is set, project managers will have a complete picture of the project’s schedule. It is then used to estimate the minimum time required to complete a task.
17) Earned Value & Earned Value Management (EVM)
Earned value refers to a method in project management used to track the amount of work completed. It is one of the quickest ways to check if you are ahead of schedule or behind. Earned value and project cost management are connected; earned value helps you understand if you have gone over your planned budget.
Earned Value Management (EVM) is an approach that uses schedule, time, and cost to measure project progress. The EVM methodology foresees the future based on actual values and planned values, so project managers can make adjustments accordingly.
18) Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS)
Organizational Breakdown Structure is a model that describes the framework of the organization for project planning, resource allocation, budget estimation, and more. It is a structured hierarchical model that brings together all elements involved in a project.
What steps are involved in creating OBS?
- The entire organization is drawn as a hierarchy
- All departments and project teams are defined
- Mention the functional and approval groups for every user
19) PERT Chart
A PERT (Project Evaluation and Review Technique) chart is a visual aid in project management to track tasks and timelines. Though it might draw some similarities to the Gantt chart, both differ in terms of features and elements.
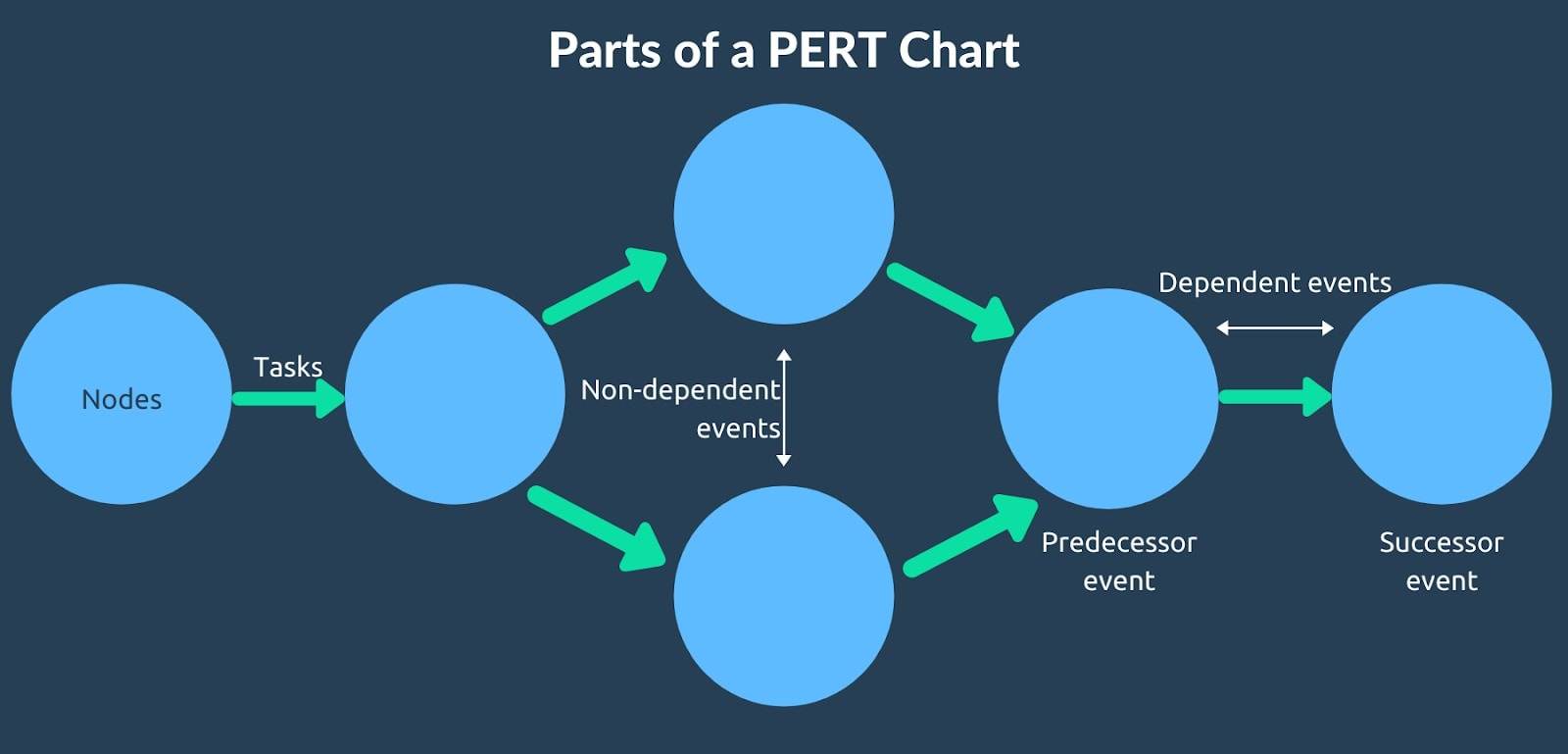
Source: HubStaff
How is a PERT chart created?
- Identify project activities.
- Identify dependencies of activities.
- Use the identified activities to map out your chart.
- Set timelines for all activities.
20) RACI Chart
Responsible Accountable Consulted Informed (RACI) chart is used to assign responsibilities to team members. It is created by identifying roles and delegating tasks to appropriate team members.
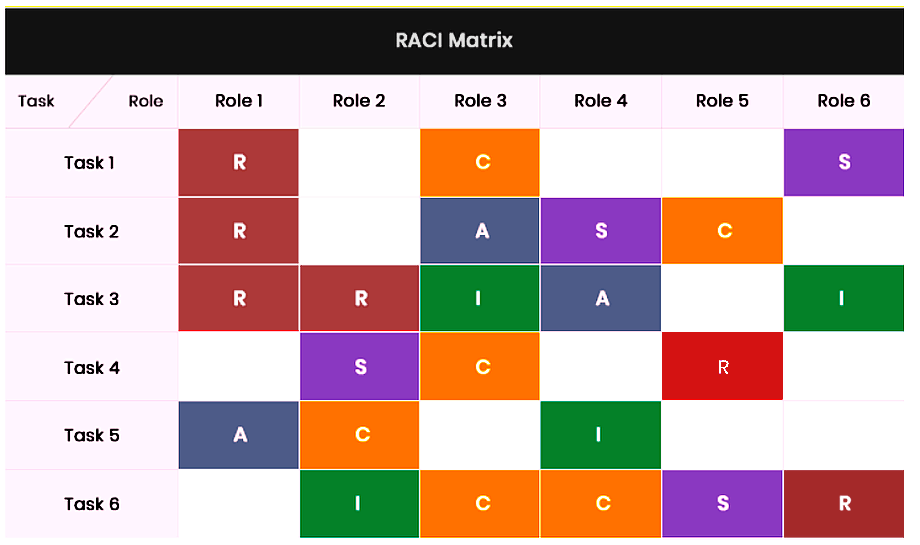
Source: BVOP
What does RACI stand for?
- Responsible ─ Every task holds at least one or more team members responsible.
- Accounted ─ A team member is responsible for delegating tasks and approving deliverables.
- Consulted ─ A designated team member is responsible for reviewing deliverables and giving feedback.
- Informed ─ These team members need to know how tasks are executed.
21) Statement of Work (SoW)
A statement of work is a detailed document that captures all the aspects of a project. It is created to plan the landscape of the project, so you can plan and execute it. As the name suggests, the statement of work requires a great deal of writing. It is one of the primary means to share what a project entails, including all team members and stakeholders. It acts as a solid structure upon which a project plan is built. With careful documentation and clarity of detail, a statement of work can keep conflicts at bay during project execution.
How Does a PMP Bootcamp Help You Learn Project Management Buzzwords?
To increase the effectiveness of your tasks and to comprehend terminologies, it is essential to become acquainted with popular project management buzzwords. PMP bootcamp is an instructor-led immersive learning experience that focuses on applied learning. Be it the guidance from industry experts or hands-on project experience, there are several reasons to choose PMP certification training over self-paced learning. The biggest advantage is that you get to interact with industry veterans who will provide you with a holistic understanding of essential project management skills. The bootcamps are designed to help you gain insight into project management terms and concepts. They make use of workbooks and cheat sheets to help you become familiar with all project management concepts.
If you are seeking the right PMP bootcamp to pass your PMP certification exam in one go, it is critical to pick your course wisely. GreyCampus is a premier provider of PMP certification training for aspiring project managers all over the world. It comes with 6 months of unlimited access to live bootcamps led by industry experts and one-year access to quality learning materials. The program also guarantees 35 contact hours and one-year mentorship.
Want To Become a Project Manager? Get PMP Certified Today!
