12 Key Six Sigma Tools You Need To Fare Better In Your Career
Lean and Six Sigma, both are two different approaches. The path they choose is completely different, but they work towards the same goal. Lean focuses more on the process where six sigma focuses on the quality of the output.
Lean is an approach used to achieve higher productivity using minimum resources. Eliminating wastes and reducing cycle times are the key factors in the Lean approach. Six Sigma focuses on maintaining consistency in the process. It is completely data-driven, unlike Lean, which is completely process-driven. Hence it is defined as 3.4 defects for every million opportunities.
Lean Six Sigma is a combination of productivity and quality. This is what all organizations strive to achieve, and customers expect. To achieve this, a professional has several Six Sigma tools at his or her disposal.
Here are the 12 most important Lean Six Sigma tools:
1) The 5 Whys
The 5 whys is one of the most popular Lean Six Sigma tools. To solve anything, finding out exactly where the problem lies is important. The 5 whys is one such tool by the usage of which the actual problem can be found. It works in this way if you find a problem anywhere ask why it had occurred. If that answer is not the root cause of the problem, repeat the why question again. Repeat the loop until you find the root cause of the problem. You can ask why more than 5 times but in most of the cases the root cause is found before the 5 whys.
However, this cannot be applied in case of complex problems. In 5 why analysis the entire analysis is performed in only one track. In the case of complex problems, an analysis should be carried out in all possible perspectives, which is a limitation in 5 whys analysis.
Let us discuss this with an example from our daily life. “Wich and Fun” is a sandwich vendor. He got a corporate order to supply 100 sandwiches every day in the evening at 4.00 Pm. On the very first day, the contract got cancelled. Below shows the 5 whys inquiry diagram.
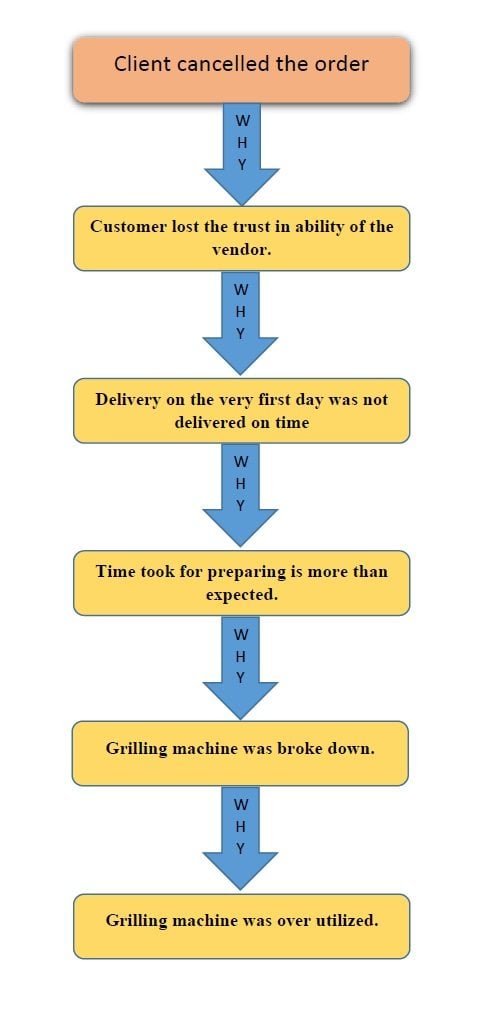
5 Whys Analysis Example

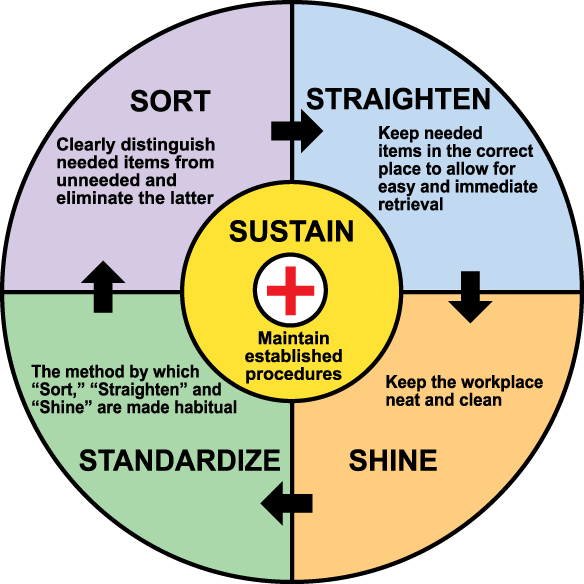
2) The 5S System
It is a methodology that consists of 5 Japanese words. They mean “Sort,” “Set in Order,” “Shine,” “Standardize,” “Sustain”. The words in the list tell how a workplace should be maintained. The effectiveness and efficiency of the work done in a place are directly affected by how the workplace is. With implementing 5S in any organization brings 5 benefits to the organization. They are:
- Reduced Costs
- Higher Quality
- Increased Productivity
- Greater Employee Satisfaction
- A Safer Work Environment
Here is how Lean Six Sigma 5S will derive these 5 benefits.
Sort: It helps the user to determine what is actually needed and what are not in the work area. Some common question which is used in this phase are
- What is the purpose of this item?
- When was this item last used?
- How frequently is it used?
- Who uses it?
- Does it really need to be here?
These questions help to determine the values of the items and help in deciding what to be kept in the work area.
Set In Order: Once all the unwanted is removed from the work area, next comes setting them according to the convenience of the people who use them. They can be segregated in several ways, according to the frequency of usage, space occupation, the colour of the objects, etc.
Shine: Everyone knows the importance of housekeeping. Having a clean and hygienic work area creates interest to the employee to accomplish the task assigned. In industries and plants, shine refers to performing regular maintenance on equipment and machinery. This prevents machinery from getting a breakdown.
Source: BeyondLean
Standardize: Now, the work area is clean. All the required equipment and tools are available in perfect condition. The work area is very clean. In the early times of 5S implementing everything will be perfectly set, and setting back things after use is also easy. In the long run, having no set of instructions in the work area leads to misplacing things and again brings the same old situation back to place. So having standardized operating procedures is very much essential to bring all the results as mentioned in the beginning of the discussion.
Sustain: The last and important step in implementing 5S in an organization to sustain. After the first 3S’s were implemented, to perform them a standardized operating system need to be framed. After the operating system was designed, it needs to be sustained in the organized. For a successful implementation of 5S in an organization, employees from various departments at various levels need to contribute to achieving the desired outputs when and where required.
Consider the same example of “Wich and Fun” as quoted under the explanation of 5 Whys analysis, and this is how a kitchen with 5s implementation and without 5s implemented looks like.
3) Pareto Chart
This is one of the most commonly used Lean Six Sigma tools. It is a combination of a bar graph and line graph. The bar graph is in descending order, and the line graph is in ascending order. The horizontal axis consists of the list of causes for the problem. Each bar represents one factor Left vertical axis represents the frequency of occurrence or the cost incurred by that defect etc. The right vertical axis represents the percentage from 0 to 100.
The contribution of each factor in the total problem will be plotted by the bars. Cumulative percentages are plotted in the form of a line graph parallel to the bar graph. All the factors till the cumulative percentage of 80 are vital few factors. These factors are the major problem causing factors. The Pareto chart identifies the major problem causing factors.
Let us consider the same above example, “Wich and Fun.” Every week there are 100 sandwiches which are thrown into the dustbin with various reasons. Below is the table.
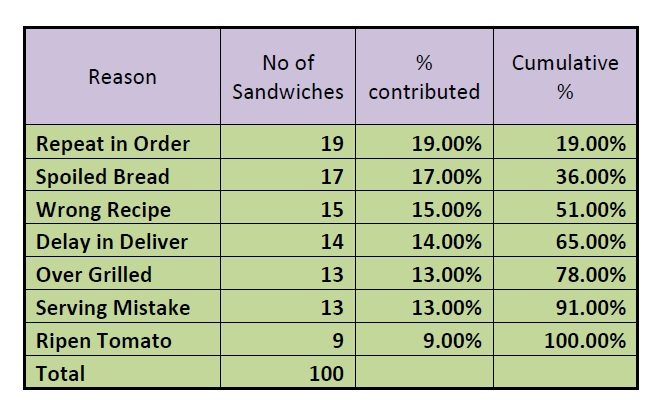
Pareto Analysis for wastage in Wich and Fun
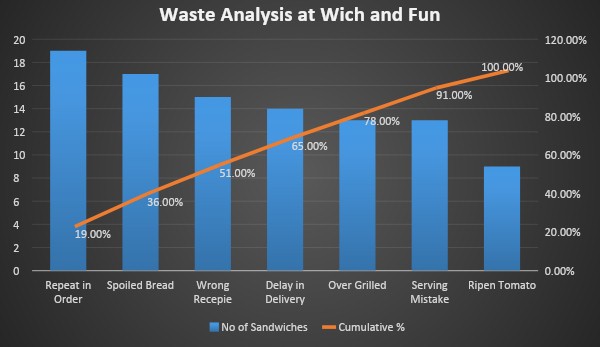
Reasons for wastage and their contribution
In the above graph, there are seven reasons which are causing wastage in the café. Among these seven reasons, the first five are contributing to almost 80% wastage. So according to the Pareto analysis, working on these reasons helps in eradicating 80% wastage in the café. This is how Pareto analysis is used.
4) Kaizen
It is a Japanese word which means “Improvement.” In a business perspective, kaizen cites all the activities which continuously improves and includes everyone in the organization. Implementation of Kaizen in an organization enables continuous observing, identifying, and implementing things. It helps organizations to grow continually.
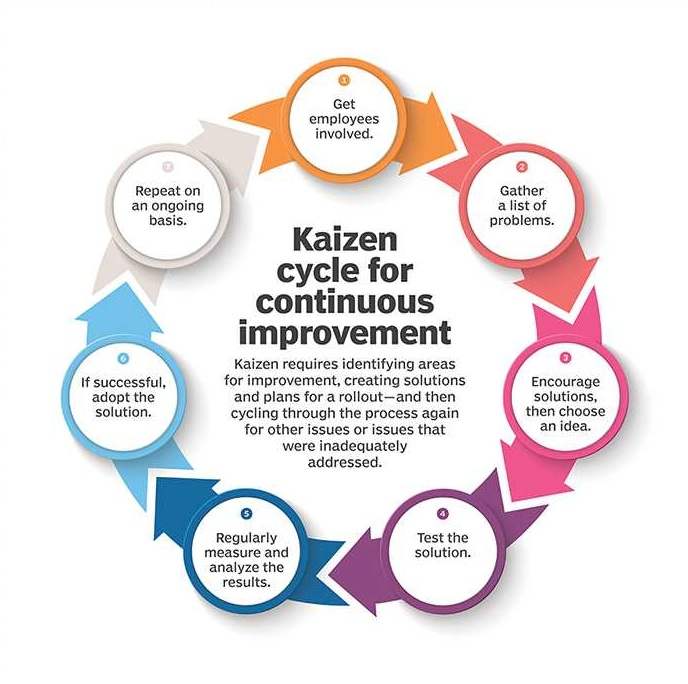
Source: TechTarget
“Wich and Fun” wants to implement kaizen in their café. Below is the plan for improving the café continuously.
1) Meet the Chef, Manager and all the employees of the cafe and note down all the problems they are facing.
2) Observing the work and workflow of the employees and study the process flow in the business.
3) Keep on updating the plan whenever it is required.
4) 5S the entire system.
5) Reduce the number of steps involved in the kitchen with the goal of providing fresh food and fast delivery.
6) Marketing and promoting the café.
In this way, the set of rules should be continuously implemented in the organization, so that improvement takes place continuously.
5) Poka-Yoke
Another Japanese term which means Mistake Proofing. This is more of preventing the mistake before happening and reduce the cost of quality. This is more frequently seen in Machines and Systems. This do not permit the user to proceed to step further if there is any mistake spotted in the previous step.
Source: The Automation Blog
Consider the five major reasons which are causing wastage in ”Wich and fun,”
- Repeat in Order ─ This can be prevented by taking the order attached to the customer mobile number using a digital medium. This prevents the repeat in order happening.
- Follow Just-In-Time ─ This helps in improving the taste too because of the food being fresh.
- Assign and Map ─ Assign some codes to the recipe and map the recipe code with the ingredients. Also, First In First Out should be followed so that the wrong production of sandwiches can be prevented.
The above steps by now will reduce the making time. Hence this defect will be overcome. The grilling machines should be automatic to stop grilling after reaching a certain temperature. Doing that will completely skip the option of over grilling.
6) Heijunka
Heijunka is a popular tool used in Lean Six Sigma to equalize the production process. It reduces load and helps you manage changes effectively. With this technique, short segments of standardized work are used to meet customer demands.
Heijunka is one of the most effective Lean Six Sigma tools that keep the notorious development ‘death march’ at bay. What is ‘death march’? It is a situation, likely to show up toward the end of a development cycle, caused by the accumulation of important tasks.

Source: Market Business News
The following are common causes for the unevenness in production processes:
- Different tasks require different amounts of time.
- One cannot expect customer orders to show up in an ordered fashion.
- Different employees have different capacities.
- Teams could encounter an unprecedented challenge or dearth of resources.
Why should you tend to the unevenness in the production process with Heijunka? A system contaminated with disruptions can never be stable; an unstable system can never birth a healthy product or service.
7) PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) Cycle
The PDCA cycle is a Six Sigma tool for continuous improvement of processes. Also called the Deming Cycle, this critical tool finds its application predominantly in management and manufacturing to steer progress.
The following instances demand the use of the PDCA cycle:
- At the onset of an improvement project
- To control a cultural shift
- To enhance the quality of a process that could use more efficiency
- To identify the causes of problems
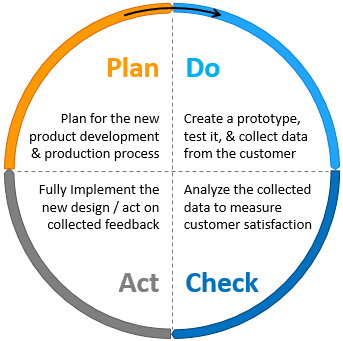
Source: CIToolkit
What are the steps in a PDCA cycle? The cycle derives its name from the steps in this method. They are:
- Plan ─ This step involves identifying the problem and understanding its impact on your processes. Gather all the information you can get your hands on about the problem. Try to identify the metrics you will use to measure the success of your countermeasures. Make sure your objectives are measurable and realistic.
- Do ─ This is the stage where you execute your measures; it commences with a simple test project to reduce risks and gauge your success.
- Check ─ In this step, you consistently check the results of your processes. This demands the availability of enough data so your measurement is accurate.
- Act/Adjust ─ This is the stage where you fine-tune your actions. If your test project succeeds, you implement it on a large scale. If not, you repeat the PDCA cycle but with better measures.
8) Kanban Pull System
A tool that originated in the 1940s, the Kanban pull system is a Lean Six Sigma tool that is used to guarantee the smooth flow of work. It encourages professionals to pull in work only if there is an absolute demand for it.
It reduces waste by letting you take on work only in the following circumstances:
- Whenever there is customer demand
- When goods are required in a certain step
What makes the pull system a great tool and strategy? In a push system, the production is reliant on expected demands, which may not always align with the actual demand. This disparity can create financial constraints. The pull system, on the contrary, encourages you to depend on actual demand. The tool prioritizes ‘just-in-time’ over ‘just-in-case’.
The pull system helps optimize storage costs; that is, from the materials you need for production to the number of personnel you need to complete a task, everything can be accurately estimated beforehand.
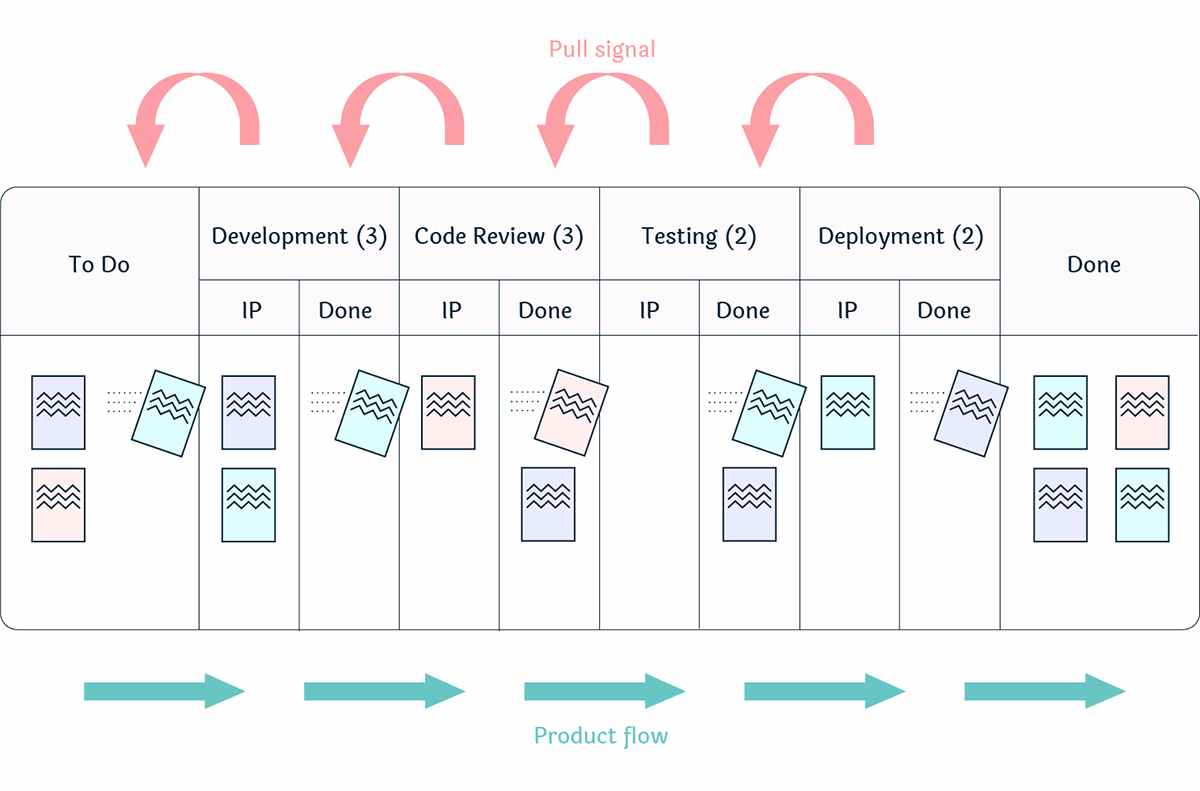
Source: Nave
The following are the steps to follow to implement the Kanban pull system:
- Visualize ─ Visualizing your workflow is the first step in implementing the Kanban pull system. The trick is to map out your flow as accurately as possible. Determine your steps in each stage of your processes; add columns and lanes to make it comprehensible.
- Move from Push to Pull ─ Redefine the way you add new tasks; take on new tasks only upon demand, never push tasks to a team. This will help you boost the efficiency of your team and bring down inventory costs.
- Establish WIP (Work in Progress) Limits ─ In this stage, you need to define how you work in progress limits. In order not to clog your development cycle, the rate at which your items move through the board needs to be kept in check.
Once you have the Kanban pull system up and running, you can apply other Lean Six Sigma principles to maximize quality.
9) Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is one of the most popular Lean Six Sigma tools used in visualizing tasks. Also called material information flow mapping, this tool helps you get ahead of the competition in your market. It lets you create an in-depth visualization of all the tasks in your processes, making your status-check a quick and easy activity. The visualization is in the form of a flowchart where all the elements required to create a product or service are represented.
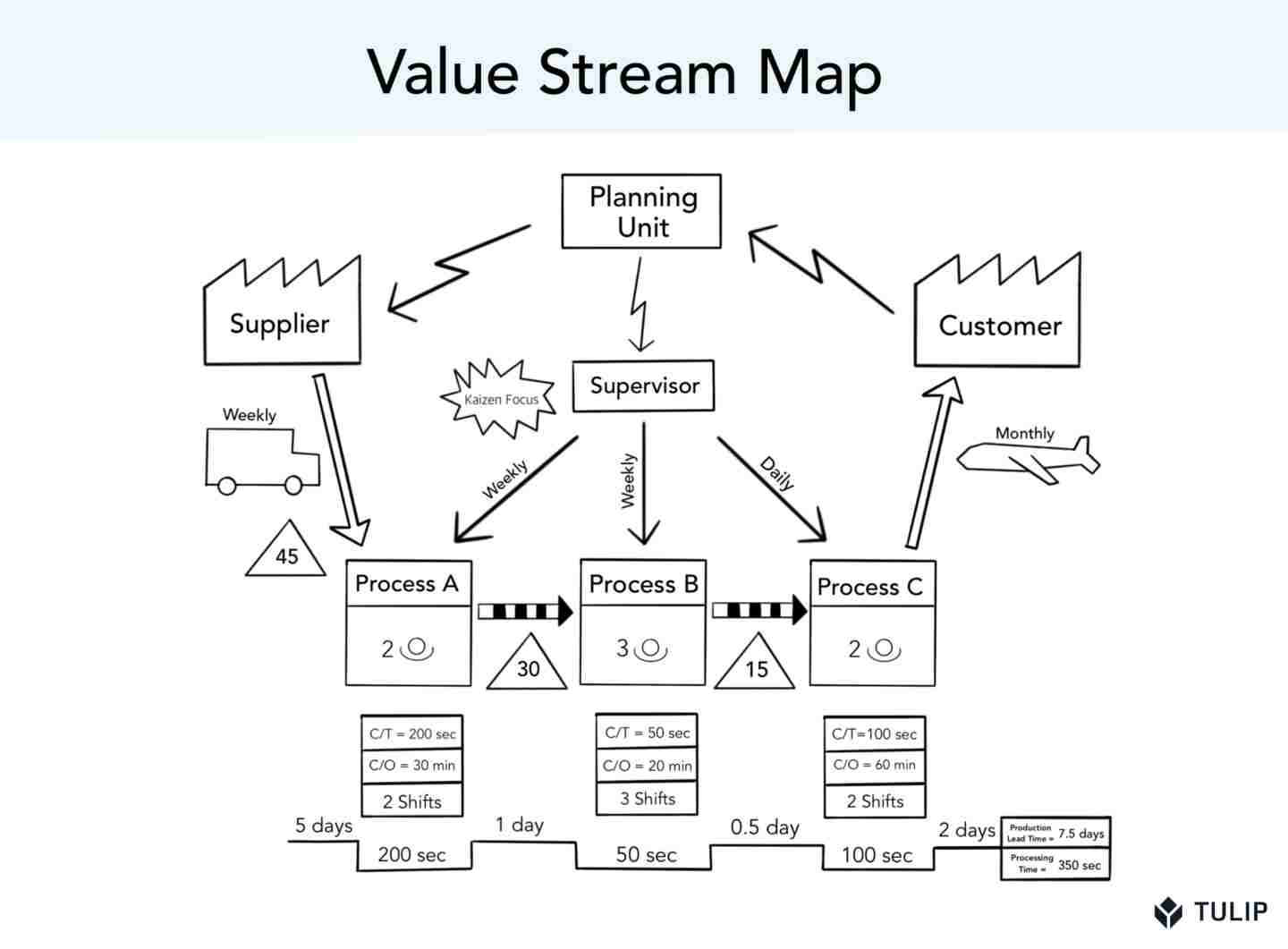
Source: Tulip
What are the advantages of value stream mapping?
- It helps in effective communication.
- It facilitates continuous improvement of processes.
- It enables change of culture within the organization.
- It allows easy visualization of delays and constraints.
A value stream map can be created on a template, software, or even on a whiteboard. Before you create the visualization, create an outline that includes all the processes, stakeholders, and the interrelation between both. Edraw and Lucidchart are two popular software programs used for value stream mapping.
10) SMED (Single Minute Exchange of Dies)
Single Minute Exchange of Dies is one of the best Six Sigma tools used to optimize production equipment. It facilitates the smooth and efficient transfer from one product to another in manufacturing. This timely transfer is what enables the optimization of production equipment. It enhances product quality and improves the flow of processes. It minimizes waste by reducing system changeover times.
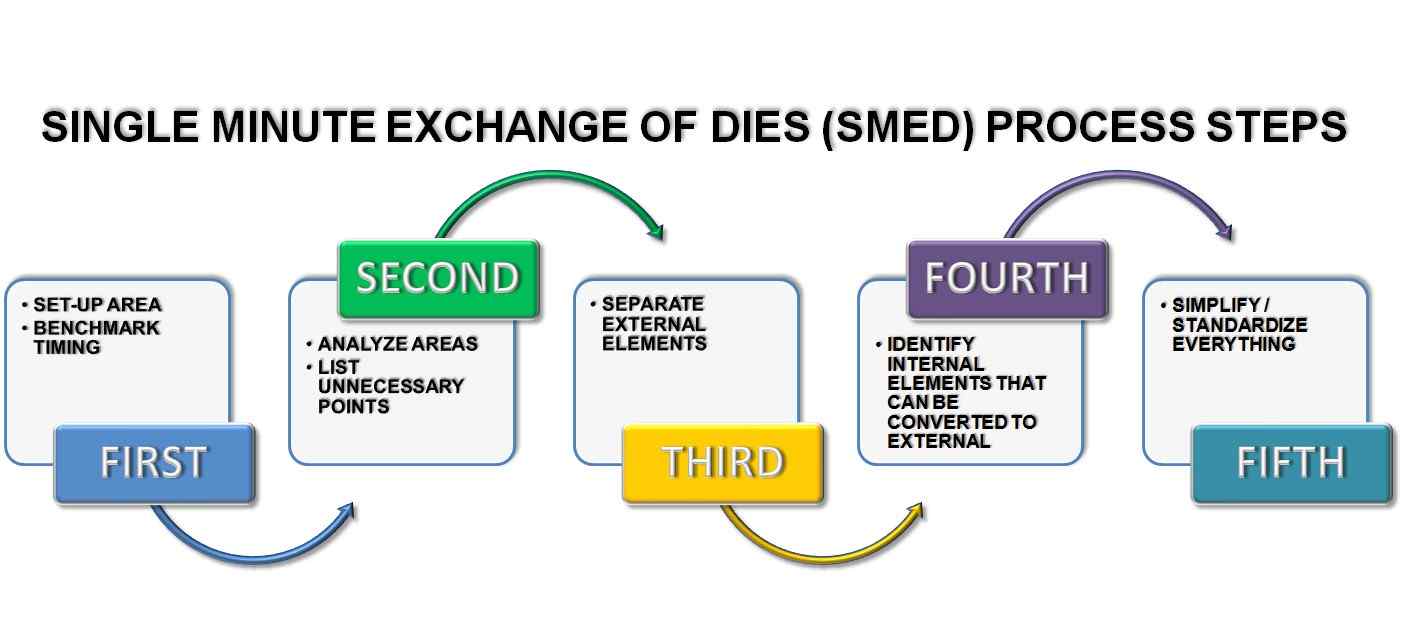
Source: WhatIsSixSigma
What are the advantages of SMED in Lean manufacturing?
- Minimizes equipment downtime thus eliminating waste.
- Product changes are easily enabled with Just-in-Time manufacturing. With flexible scheduling, processes are converted into job shops, which in turn paves the way for more production output.
- Production quality is optimized.
A tool that originally evolved in the manufacturing industry, SMED is one of those Lean Six Sigma tools that is seamlessly used in various industries to eliminate waste.
11) Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance is the maintenance of production and quality systems using a combination of machines, people, equipment, and processes. It uses preventive and predictive maintenance techniques to improve the effectiveness of systems. The ultimate goal of using this tool is to reduce waste, defects, failures, and loss. It is also helpful in doing away with delays.
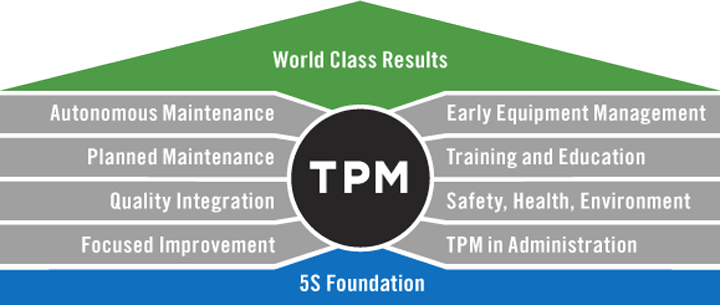
Source: LeanProduction
The following are steps in TPM:
- Analyzing the Current State of Affairs ─ This step involves understanding the business, its environment, and the different processes involved. Contacts are established with various process owners and operators.
- Accountability for the TPM Process ─ Each team should completely be responsible for the processes they carry out. They must also have a maintenance vision, which the team should be independently able to achieve.
- Identifying Critical Equipment and Other Resources ─ This is the most critical step in total productive maintenance; important pieces of equipment are identified, and their condition is assessed. The best method is to use a scoring system that ranks every piece of equipment in the organization.
- Assessing Maintenance Skills ─ This stage is where the skill gap is studied; to minimize the downtime, an analysis is conducted to understand whether the organization has enough in-house support to rectify glitches and defects. If an employee needs to be trained in any maintenance skill, this is the time where you find out and fix it.
- Implementing Maintenance Techniques ─ This is the point where maintenance techniques are implemented. The implementation is based on the following pillars of total productive maintenance:
1) Safety Health Environment
2) Planned Maintenance
3) Early/Equipment Management
4) Education and Training
5) Focused Improvement
6) Administrative & Office TPM
7) Autonomous Maintenance
8) Quality Management
12) FMEA (Failure Modes and Effect Analysis)
Failure Modes and Effect Analysis is a tool that helps in identifying failures in processes and understanding how it impacts customers. To employ this tool effectively, a professional should have an in-depth understanding of every step in the process. FMEA works the best for teams that have defined their project scope.
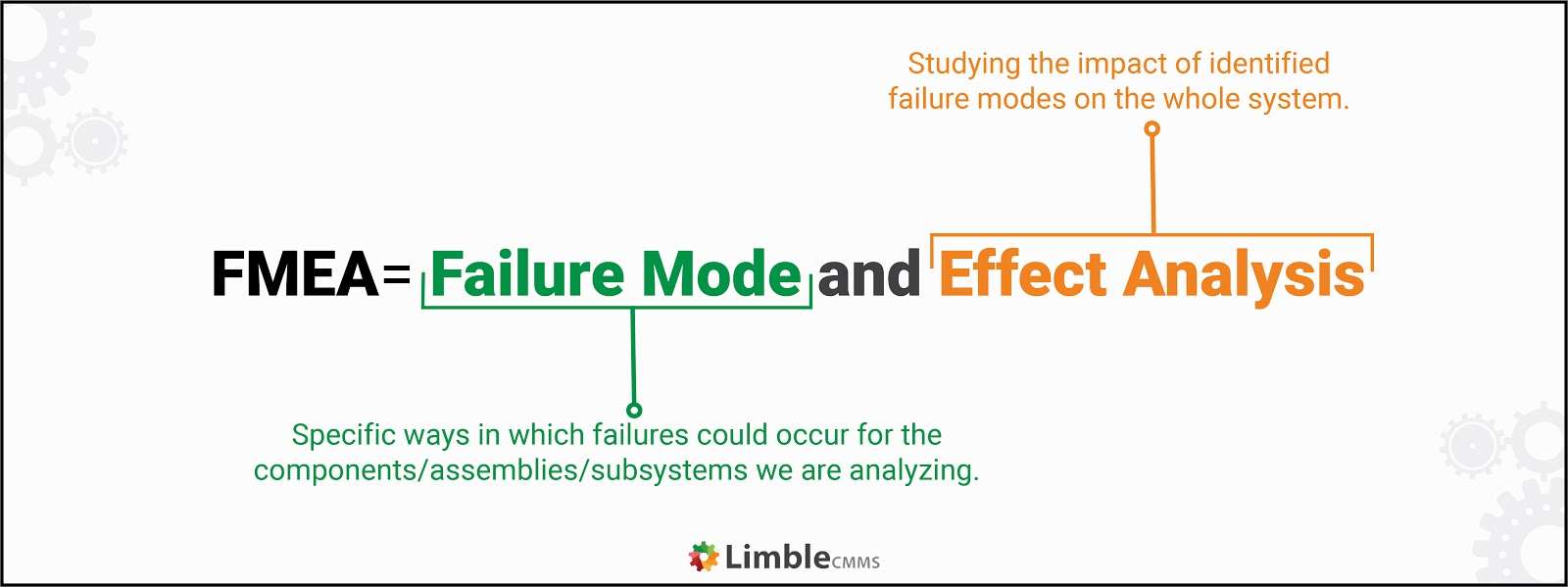
Source: LimbleCMMS
Here is how you can implement FMEA:
- Identify problems.
- Try to forecast the results of each failure.
- Analyze the severity of each failure. Rank them based on severity (10-point scale).
- Determine the probability of each failure; rank them.
- Determine the probability of each failure being noticed by the end-user; rank the probability using a 10-point scale.
After the probabilities of failure are ranked, calculate RPN (Risk Priority Number). RPN is calculated by multiplying the ranks of the three metrics: detection, severity, and occurrence. Once the RPN is estimated, each cause of failure will be assigned a priority number. This will help employees prioritize tasks.
Following these steps closely will help your team predict failures and their impact on customers. This is what makes FMEA one of the most remarkable Lean Six Sigma tools.
It is imperative to choose your training program wisely to master Lean Six Sigma tools. GreyCampus is a leading provider of career training programs for aspiring Lean Six Sigma professionals. Its Lean Six Sigma Green and Black Belt Combo Training and Certification program is designed to help you acquire Green and Black Belt certification from the International Association for Six Sigma Certification (IASSC). The program comes with one year of access to quality learning materials, 80 PMI PDUs, simulation tests, and bootcamps for 6 months.
Want To Manage Processes Better? Sign Up for a Lean Six Sigma Bootcamp Today!
