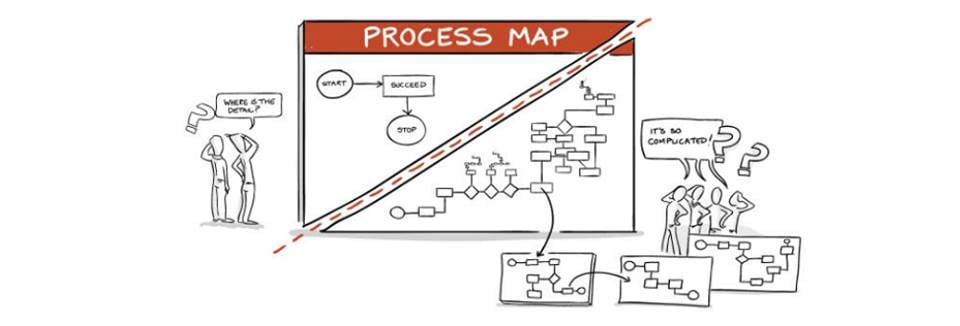
Process Maps: What are its Different Types and their Application?
Introduction
So here we are with process maps, nowadays in real life, we can see, how maps are helping to us, we build a confidence to go anywhere just because we are confident about any road. So now, you can relate how important the map is. Now, let's come to the topic, the process map will give you the idea of the process workflow, which will help to understand the process and their working. It can help the higher management, who are not involved with the process but in the business, where sometimes it is necessary to understand the process.
What is a Process Map?
A process map shows the consecutive process steps we take to complete the one task. That process can be anything, while cooking, or getting ready for office/school, everywhere we have some tasks to complete and for that, we should have consecutive or sequential process steps.
It is a visual guide for the process data. It is a series of process steps, which helps to transform Inputs into Outputs. It also helps to find the value-added and remove the non-value-added steps.
For example for making tea, we must have all the essential ingredients, then the proper steps to make the tea. Likewise, while wearing the clothes, we can have a procedure, first, wear the shirt then the trouser.
Process steps can be followed by organization standards. Sometimes we get a bill after the service, but in some processes, we first need to pay to get the service.
Process Map is used to show the sequential steps of the process at once. We can see the process maps in multiple ways. If we want to see high-level process maps, where only we should know who are the suppliers, what all are the inputs, wide process steps, what should be the outputs and all our end customers. Then we use the SIPOC. It gives the info of What is happening. This is the Level 1 process map.
Likewise, we could use a bit detailed process map, which gives the info of What and Who is responsible. This calls Level 2 process map.
In the Level 3 process map, the questions What, Who and How would be answered.
How to create and use a Process Map Template?
For different process maps, we use the different method to make the process maps. Although, the ground rules and the symbols as mentioned in the figure are the same for all types of the process maps. The arrow of the process maps should be in one direction, it should not be in the zig-zag direction.
The ‘Yes’ and ‘No’ decision should box have the same direction throughout the process maps, for example, if Yes decision is pointing at the right direction and No decision points downward then we should show every decision in the same way throughout the whole process map.
Always try to keep the same size for all the boxes. Try to give the whole detail and each and every step of the process, if we need to click once or twice to open the app, this should also mention in the process maps.
While making the swim lane process map, we should always consider, we have a map by which any new aspirant can easily understand the process without asking anyone.

Source: https://www.pinterest.com
Different types of Process Maps
Type 1 Process Map: SIPOC Map
The Level 1 process map, we see the overall process, these process maps are mostly used at the Define phase, where, we need to have a hawk eye view of the overall process. The whole process, with their inputs, suppliers, outputs, and customers with few process steps.
In the mapping hierarchy, the highest order tool is SIPOC. It gives the information which is Critical to Business, Critical to Quality and the critical to customers. And by this, we get a better understanding of all components.
You may also like: A Complete Guide to a Lean Six Sigma tool: SIPOC
Nowadays SIPOC is called SIPOC-R, where R represents Requirement.
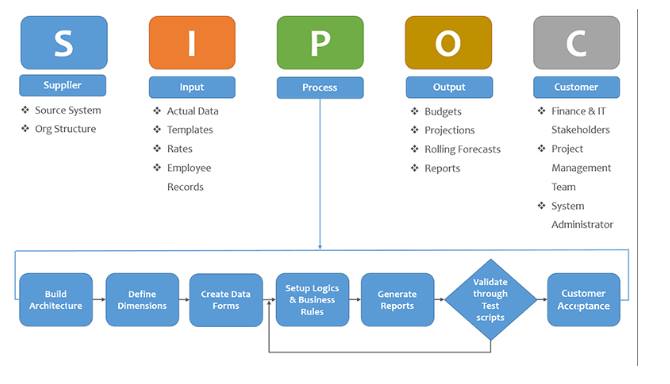
Source: http://www.karyatech.com
Type 2 Process Map: Deployment Map
These types of process maps are used for the stakeholders. It gives information on how the process works. Stakeholders are neither interested nor do they have any requirement to know the detailed process steps; however, the major process steps would be covered in these maps.
These maps would do not need to contain the whole process knowledge; therefore, it can be prepared with the help of process manager. This is a more elaborative SIPOC, where we get some more process information. There would be more process steps.
This is also a deployment process map, where we can see the connection and dependencies on other processors. In Visio, we can use the deployment with the signal or could use the different colors in normal process maps so that the other processes should be highlighted.
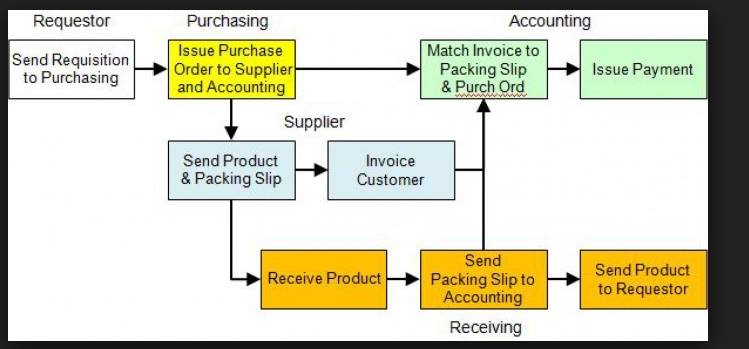
Source: https://goleansixsigma.com
Type 3 Process Map: Swimlane Map
The Level 3 process maps are those maps, which have detailed info of the process, it is the micro level process maps. It gives the whole process steps at once if a new processor can understand how to do the task at once. We generally do not much need of seeing the whole process, however, some part of the process must be needed to see at once. The detailed process maps would work in that case.
This is also called the Swimlane map, it also has layers and sequence wise representation of the process. Here we can figure it out, who does what. However, it has a drawback, due to being a detailed map, it is very huge and it is very space efficient.
To see the whole process at once take more time. And understand the process is also a bit difficult, only the expertise could understand.
These types of process maps, we use to see the gaps, issues or unnecessary steps to resolve the issue or could work and decrease the lead time/cycle time. By cut shorting the process steps could help us to decrease the number of employees.
Even sometimes the whole micro-level process map shows, in which area we need to more focus. We can find the pain area, could start the treatment of that particular while seeing that area as a whole.
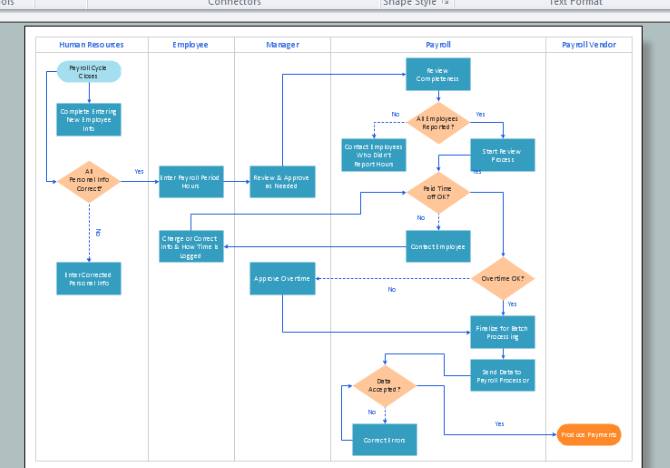
Source: https://www.conceptdraw.com
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Map is used to understand what is valuable to the process and what is non-value added. The VSM is also called the Material and Info flow map. Greater amount of skill is required for making the VSM, however, it consists of excessive info.
The Value Stream has all the actions which bring the main flows and give the service to the customers. Usually, every process has 3 types of conditions, first - What you have thought about the process? What actually the process is and how the process should be? How the process should remove the unnecessary steps while seeing the NVA in the VSM process maps?
The VSM is used in the Lean concept, it is the tool of Lean, it shows the Pull scheduling or opportunity to do the pull scheduling. It is used when we plan for process improvement. VSM is often used when planning a Lean implementation to display the current state of the process including material, information flows and any other information important for Lean implementations.
You may also like: 7 Things You Must Know About Value Stream Mapping
Here let’s discuss in brief what is Value Add and what is Non-Value Add?
- Value – Capabilities of the product or process as defined by the customer, provided in the right form, at the right time and for the suitable cost.
- Value Added and Nonvalue Added – In simple words, if the customer is willing to pay for something, it is the value-added service and if the customer is not willing to pay or there are unnecessary steps then it is counted as Non-Value-added services.
There are chances that customer would not be willing to pay, however as per the internal control those steps are required, such NVAs are called NVAR.
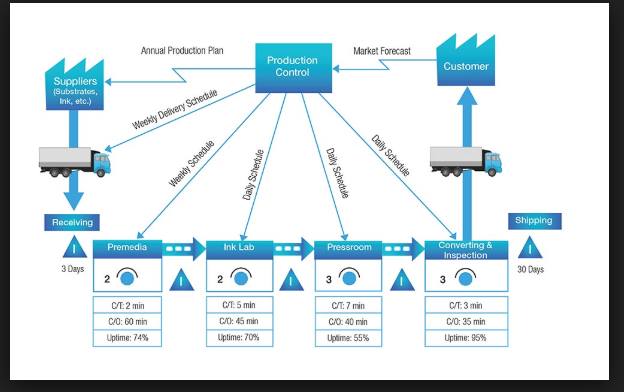
Source: https://www.xrite.com
Choosing the Right Process Map
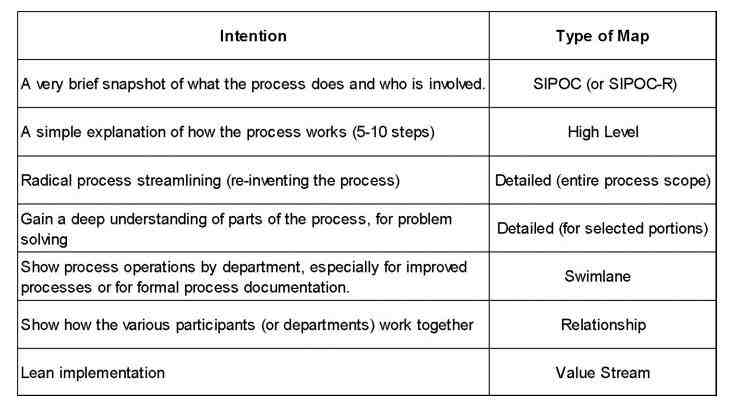
Source: https://goleansixsigma.com
Benefits of using Process Maps
It gives the visibility of the end to end process, it provides information of the business and ultimately the customer and how do they get impacted from the process.
It also gives us the reason for the change, if we want to remove some steps, or want to change the process method, we could show it in the map and give the insight the reasons for doing so, hence it would work as a proof of change.
It gives the insight of the whole process and who is responsible for that activity that also can easily be traced. Since in process map, we can find out who was responsible for those actions and we should work on it accordingly.
We can also use the process maps for induction and training purposes also, for new joiners they could get the info of the process by the process map.
The process maps in any organization are used as a blueprint, later no one looks into the map since they already know the process, however, we always try to update the process map as this is easy to understand and keep easy to use.
Over the period of time, we get updates, or changes in the process according to those changes we need to maintain the process maps also for new joiners and to keep the record of the process with the different versions so that we can see all the changes made during those time.
You may also like: How to measure Process Capability and Process Performance?
In a continual improvement, we can use it to see the improvement area, also for compliance and ISO audit purpose Process map can be used.
The process map is very useful while doing the FMEA, to see all steps and then check their failure mode and the effect analysis.
How does it benefit your project?
As mentioned above, process maps give the insight of the whole process, we can see the process as a whole and we can find the improvement areas and loopholes of the process, based on that we can run the project.
By FMEA we find the risk in the process steps failure, based on that we decide how we can improve the process and avoid or prevent the risks.
Top Steps to Successful Business Process Mapping
In the successful business, all types of process maps are useful, everything depends upon the situation and their usage.
At some places, we only need to see the VSM, whereas in some places we need the detailed information of the process where we can use swim lane/ high-level process maps, as mentioned above, for continuous improvement we must see our process, that can be seen from amongst the mentioned any process and make improvement accordingly.
You may also like: DMAIC – A Six Sigma Process Improvement Methodology
Conclusion
Hence in every business, we need process maps to know the entire procedure and to follow and run the process accordingly. Every process map has its benefits and constraints, hence as per their use in the business and situation, we must use the best process maps. We can make the process maps in the Visio, however, we can also make in a simple MS word format.
Become a Quality expert | Get trained by industry experts