Total Quality Management vs Quality Control
Introduction
There are many aspects of Quality. These can be at different levels (Product, Organization, etc). Different organizations adhere to quality standards based on their requirements. Let me introduce and define the meaning of Quality, Quality Control, and Total Quality management. We shall understand what each means and how they differ from each other.
Quality
What is quality?
Project Management is the art and science of managing projects. There is an emphasis on quality, cost, and time. Quality is one of the factors of the “triple constraint” that govern the art of project management. Quality is defined as the degree to which the project meets the requirements (PMBOK, 2009).
Dr. Edward Deming is the Father of quality management. In 1950, he defined quality as something which fits for the purpose. Quality is interpreted as the non-inferiority or superiority of something. This is especially true for business, engineering, and manufacturing. It is also defined as being suitable for its intended purpose. Fitness for purpose, while satisfying customer expectations. Quality is understood differently by different people. It is a perceptual, conditional, and somewhat subjective attribute.
Let us take an example of a tube light manufacturer - We will use this example at various places. So, it will act as a relative reference. Now the manufacturer may mention that it is 40 Watts tube light and will run for 10000 hours. Now the definition of quality says that it should be suitable for its intended purpose. So, from the customer perspective, it is said to have good quality if:
- It emits light which a 40 Watts tube light should give
- Should run for 10000 hours
- Should always run whenever you switch it on
- The lesser heat it generates the better
- Should not break down in between
Consumers may focus on the specification quality of a product/service. They would compare it to competitors in the marketplace. Producers might measure the conformance quality or degree to which the product/service was produced correctly. Support personnel may measure quality in terms that a product is reliable, maintainable, or sustainable.
For software, quality means, the functionality and features of a software product. Its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs of users. For technical coders, the lesser the defects the better is the quality.
Hopefully, now you can relate to what quality means!! It is considered as an important concept for every organization. It can be expressed as a measurement that is used to estimate the standards of a particular product or service. Now let us understand Quality Control.
Quality Control
What is quality control?
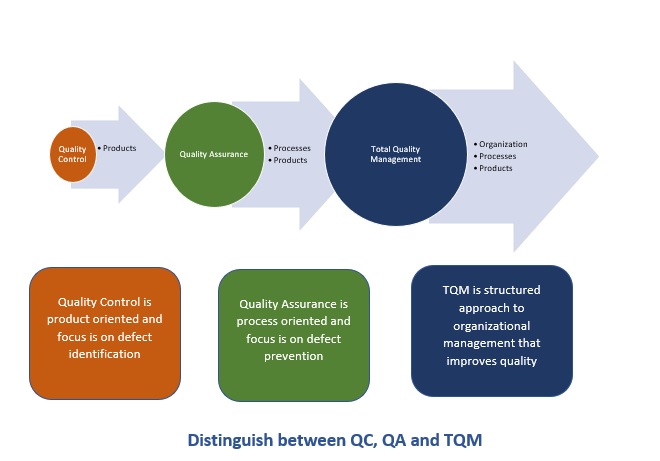
Quality control is also known as QC in short. This is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in the production. QC focuses on ensuring that a product meets the prescribed technical standard of quality. It should also meet the customer's requirements. It involves the physical checking of activities at each specified stage of production. This covers cycles from receiving materials and manufacturing to testing, packing, and shipping. So, quality control is product-oriented and focuses on defect identification.
Let us go back to our example of a tube light. What is Quality control here? On the manufacturer's side it could be something like, someone testing to see:
- Tubelight works when switched on
- Tubelight emits light usually a 40 W tube light should emit
- Does not get too heated
- Packaging is proper
The manufacturer will decide what sample size he would like to take. There could be many such checks. The point to note here is that they are testing to identify defective products. What about quality control in software? They can have defect reviews to check defects in codes, functionality not working as intended, etc. This is identified during testing.
There is an additional concept of quality assurance. This involves processes to prevent defects. Quality assurance is process-oriented and focuses on defect prevention. It focuses on making operations more efficient and reliable. Now, when we move further ahead, we see Total Quality Management (TQM). Let us now do a deep dive in this area.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
The exact origin of the term "Total Quality Management" is uncertain. It may be inspired by Armand V. Feigenbaum's multi-edition book Total Quality Control and Kaoru Ishikawa's What Is Total Quality Control? The Japanese Way. It may have been first coined in the United Kingdom. Their Department of Trade and Industry had used it during its 1983 "National Quality Campaign". Or it may have been first coined in the United States by the Naval Air Systems Command to describe its quality-improvement efforts in 1985.
How does TQM help in organizations
TQM is at an organizational level. It is infusing quality aspects across the organization. It can also be extended to suppliers to ensure good quality inputs. The benefits of these are seen across the organization. It includes its products, processes, internal operations, and all other departments. TQM is a comprehensive and structured approach to organizational management. It seeks to improve the quality of products and services. It involves continued feedback and refinements for improvement.
TQM consists of organization-wide efforts. It installs and makes permanent a climate where employees continuously improve their ability. This helps to provide on-demand products and services that customers will find of particular value. "Total" emphasizes that departments are obligated to improve their operations. It includes all departments like sales and marketing, accounting and finance, engineering, and design. "Management" emphasizes that executives are obligated to actively manage quality. These could be through funding, training, staffing, and goal setting.
While there is no widely agreed-upon approach, TQM efforts typically draw heavily on the previously developed tools and techniques of quality control. Total Quality Management Definition can be - "A system of management based on the principle that every member of staff must be committed to maintaining high standards of work in every aspect of a company's operations"
Total Quality Management - The Approach
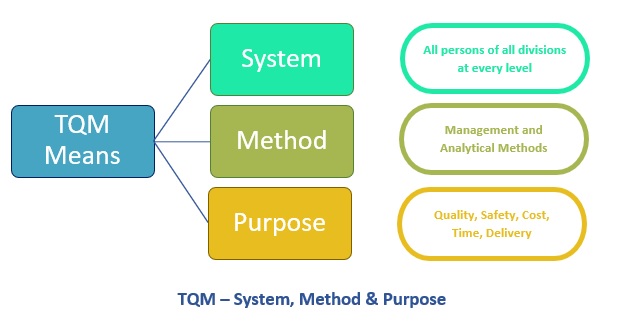
Total Quality Management is a management approach. It builds with the three different things, for example, system, method, and purpose. Firstly, the system includes all persons of all divisions at every level. Secondly, the method runs itself with the management method and analytical method. Thirdly, purpose absorbs the quality, cost, environment, delivery, and safety.
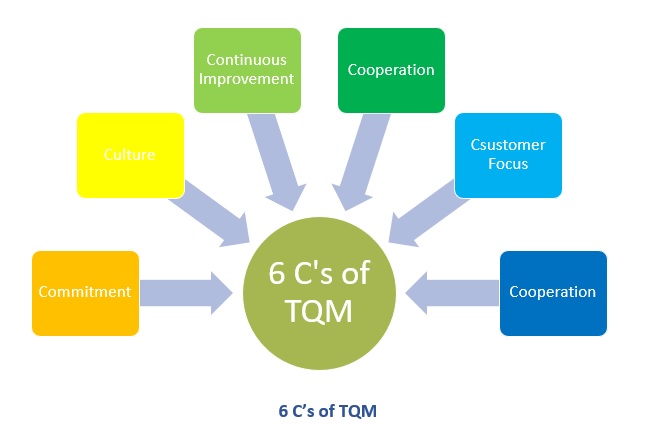
The 6 C’s of TQM are:
- Commitment
- Culture
- Continuous improvement
- Cooperation
- Customer focus
- Control
Differences between Total Quality Management and Quality Control
.png)
In a nutshell:
TQM is a philosophy that believes in a company-wide responsibility toward quality. It fosters a quality culture throughout the organization. It involves continuous improvement in the quality of work of all employees with a view to best meeting the requirements of customers.
Become a certified Quality Management Professional. Check out our courses.
